Reductive dehalogenation of chlorobenzene congeners in cell extracts of Dehalococcoides sp. strain CBDB1
- PMID: 12732577
- PMCID: PMC154522
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.5.2999-3001.2003
Reductive dehalogenation of chlorobenzene congeners in cell extracts of Dehalococcoides sp. strain CBDB1
Abstract
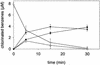
Enzymatic reductive dehalogenation of tri-, tetra-, penta-, and hexachlorobenzenes was demonstrated in cell extracts with low protein concentration (0.5 to 1 micro g of protein/ml) derived from the chlorobenzene-respiring anaerobe Dehalococcoides sp. strain CBDB1. 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene dehalogenase activity was associated with the membrane fraction. Light-reversible inhibition by alkyl iodides indicated the presence of a corrinoid cofactor.
Figures

References
-
- Adrian, L., U. Szewzyk, J. Wecke, and H. Görisch. 2000. Bacterial dehalorespiration with chlorinated benzenes. Nature 408:580-583. - PubMed
-
- Adrian, L., and H. Görisch. 2002. Microbial transformation of chlorinated benzenes under anaerobic conditions. Res. Microbiol. 153:131-137. - PubMed
-
- Bunge, M., L. Adrian, A. Kraus, M. Opel, W. G. Lorenz, J. R. Andreesen, H. Görisch, and U. Lechner. 2003. Reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated dioxins by an anaerobic bacterium. Nature 421:357-360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

