Overlapping roles of CXCL13, interleukin 7 receptor alpha, and CCR7 ligands in lymph node development
- PMID: 12732660
- PMCID: PMC2193976
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021294
Overlapping roles of CXCL13, interleukin 7 receptor alpha, and CCR7 ligands in lymph node development
Abstract
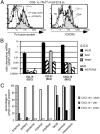
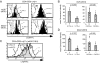
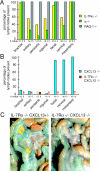
Lymphoid tissue development is associated with local accumulation of CD4+ CD3- IL-7R alpha hi hematopoietic cells that deliver lymphotoxin (LT)alpha 1 beta 2 signals to resident stromal cells. Previous studies have established an important role for CXCL13 (BLC) in the development of Peyer's patches (PP) and some peripheral lymph nodes (LNs), but the chemokine requirements for several LN types, including mesenteric LNs, remain undefined. Using CXCL13-/- mice that additionally carry the paucity of LN T cell mutation (plt/plt), we discovered that CCR7 ligands function in peripheral LN development. We also tested for a genetic interaction during LN development between CXCL13 and a cytokine receptor required in PP development, IL-7R alpha. Mice deficient for both CXCL13 and IL-7R alpha displayed a striking absence of LNs, including mesenteric LNs. These data extend the role of CXCL13 to the development of all LNs and establish a previously unappreciated role for IL-7R alpha in this process. Both circulating and LN CD4+ CD3- IL-7R alpha hi cells are shown to express LT alpha 1 beta 2 in an IL-7R alpha-dependent manner. Furthermore, CXCL13 was found to be sufficient to mediate CD4+ CD3- IL-7R alpha hi cell recruitment in vivo to an ectopic site. These findings indicate that CXCL13 and CCR7 ligands promote accumulation of CD4+ CD3- IL-7R alpha hi cells, delivering IL-7R alpha-dependent LT alpha 1 beta 2 signals critical for LN development.
Figures


References
-
- Fu, Y.-X., and D.D. Chaplin. 1999. Development and maturation of secondary lymphoid tissues. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:399–433. - PubMed
-
- Mebius, R.E., P. Rennert, and I.L. Weissman. 1997. Developing lymph nodes collect CD4+CD3− LTbeta+ cells that can differentiate to APC, NK cells, and follicular cells but not T or B cells. Immunity. 7:493–504. - PubMed
-
- Nishikawa, S., K. Honda, H. Hashi, and H. Yoshida. 1998. Peyer's patch organogenesis as a programmed inflammation: a hypothetical model. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 9:213–220. - PubMed
-
- Fukuyama, S., T. Hiroi, Y. Yokota, P.D. Rennert, M. Yanagita, N. Kinoshita, S. Terawaki, T. Shikina, M. Yamamoto, Y. Kurono, et al. 2002. Initiation of NALT organogenesis is independent of the IL-7R, LTβR, and NIK signaling pathways but requires the Id2 gene and CD3− CD4+CD45+ cells. Immunity. 17:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Finke, D., H. Acha-Orbea, A. Mattis, M. Lipp, and J. Kraehenbuhl. 2002. CD4(+)CD3(−) cells induce Peyer's patch development. Role of alpha4beta1 integrin activation by CXCR5. Immunity. 17:363–373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

