Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling intensity determines intracellular protein interactions, ubiquitination, and internalization
- PMID: 12734385
- PMCID: PMC164476
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1031790100
Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling intensity determines intracellular protein interactions, ubiquitination, and internalization
Abstract
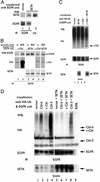
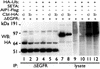
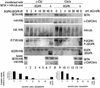
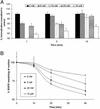
Ligand activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) causes the binding of Cbls, which leads to EGFR polyubiquitination and internalization through endophilin complexes that contain the adaptor protein SH3-domain encoding, expressed in tumorigenic astrocytes/Cbl-interacting protein of 85 kDa/regulator of ubiquitous kinase (SETA/CIN85/Ruk). In cells grown at high density, high levels of SETA interfered in the recruitment of Casitas B-lineage (Cbl) proteins to the EGFR and reduced its polyubiquitination, suggesting that SETA has a regulatory function in the formation of the EGFR-Cbl-endophilin complex and in EGFR down-regulation. In a situation where there is EGFR signaling but no internalization or down-regulation, as is the case with the EGFR with exons 2-7 deleted (DeltaEGFR) oncogene, these proteins were absent altogether. By using mAb 806, which recognizes an EGFR-activation state and preferentially immunoprecipitates DeltaEGFR, we show that DeltaEGFR did not interact with Cbls, SETA, or endophilin A1, providing a mechanistic explanation for its lack of internalization. As would be expected by the absence of Cbl proteins in the DeltaEGFR complex, the mutant receptor was also not polyubiquitinated. The intracellular C terminus and tyrosine autophosphorylation pattern of DeltaEGFR are similar to wild-type EGFR, but it signals at a lower intensity as determined by levels of EGFR phosphotyrosine. To test the implication that the lack of interaction with the Cbl-SETA-endophilin complex is because of differences in signal intensity, EGFR-expressing cells were treated with tyrphostin AG1478 EGFR inhibitor. Attenuation of wild-type EGFR signal to levels similar to that found in DeltaEGFR resulted in the dissociation of SETA and Cbl proteins and a concomitant attenuation of receptor internalization.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alix/AIP1 antagonizes epidermal growth factor receptor downregulation by the Cbl-SETA/CIN85 complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Oct;24(20):8981-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.20.8981-8993.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15456872 Free PMC article.
-
Cbl-family ubiquitin ligases and their recruitment of CIN85 are largely dispensable for epidermal growth factor receptor endocytosis.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Dec;57:123-34. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.10.019. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25449262 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin ligase activity of c-Cbl guides the epidermal growth factor receptor into clathrin-coated pits by two distinct modes of Eps15 recruitment.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 31;279(53):55465-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409765200. Epub 2004 Oct 1. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15465819
-
Simulating EGFR-ERK signaling control by scaffold proteins KSR and MP1 reveals differential ligand-sensitivity co-regulated by Cbl-CIN85 and endophilin.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22933. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022933. Epub 2011 Aug 1. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21829671 Free PMC article.
-
[Ubiquitination-mediated degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2005 Feb;27(1):120-7. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2005. PMID: 15782507 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Targeting EGFR for treatment of glioblastoma: molecular basis to overcome resistance.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012 Mar;12(3):197-209. doi: 10.2174/156800912799277557. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22268382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of CXCR4-Mediated Gi1 Activation by EGF Receptor and GRK2.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2020 Apr 27;3(4):627-634. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.0c00021. eCollection 2020 Aug 14. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 33073183 Free PMC article.
-
Scavenger receptor class F member 2 (SCARF2) as a novel therapeutic target in glioblastoma.Toxicol Res. 2022 Feb 25;38(2):249-256. doi: 10.1007/s43188-022-00125-5. eCollection 2022 Apr. Toxicol Res. 2022. PMID: 35419275 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolysis of TAM receptors in autoimmune diseases and cancer: what does it say to us?Cell Death Dis. 2025 Mar 5;16(1):155. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07480-9. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40044635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EGFR Activation Leads to Cell Death Independent of PI3K/AKT/mTOR in an AD293 Cell Line.PLoS One. 2016 May 6;11(5):e0155230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155230. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27153109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Libermann, T. A., Nusbaum, H. R., Razon, N., Kris, R., Lax, I., Soreq, H., Whittle, N., Waterfield, M. D., Ullrich, A. & Schlessinger, J. (1985) Nature 313, 144–147. - PubMed
-
- Schlegel, J., Merdes, A., Stumm, G., Albert, F. K., Forsting, M., Hynes, N. & Kiessling, M. (1994) Int. J. Cancer 56, 72–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

