Mouse Aortic Ring Assay: A New Approach of the Molecular Genetics of Angiogenesis
- PMID: 12734572
- PMCID: PMC145553
- DOI: 10.1251/bpo30
Mouse Aortic Ring Assay: A New Approach of the Molecular Genetics of Angiogenesis
Abstract
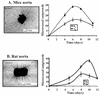
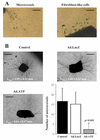
Angiogenesis, a key step in many physiological and pathological processes, involves proteolysis of the extracellular matrix. To study the role of two enzymatic families, serine-proteases and matrix metalloproteases in angiogenesis, we have adapted to the mouse, the aortic ring assay initially developed in the rat. The use of deficient mice allowed us to demonstrate that PAI-1 is essential for angiogenesis while the absence of an MMP, MMP-11, did not affect vessel sprouting. We report here that this model is attractive to elucidate the cellular and molecular mechanisms of angiogenesis, to identify, characterise or screen "pro- or anti-angiogenic agents that could be used for the treatment of angiogenesis-dependent diseases. Approaches include using recombinant proteins, synthetic molecules and adenovirus-mediated gene transfer.
Figures

References
-
- Folkman J. Toward an understanding of angiogenesis: search and discovery. Perspect Biol Med. 1985;29:10–36. - PubMed
-
- Passaniti A, Taylor RM, Pili R, Guo Y, Long PV, Haney JA, Pauly RR, Grant DS, Martin GR. A simple, quantitative method for assessing angiogenesis and antiangiogenic agents using reconstituted basement membrane, heparin, and fibroblast growth factor. Lab Invest. 1992;67:519–528. - PubMed
-
- Nicosia RF, Ottinetti A. Growth of microvessels in serum-free matrix culture of rat aorta: A quantitative assay of angiogenesis in vitro. Lab Invest. 1990;63:115–122. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

