The solution structure of an essential stem-loop of human telomerase RNA
- PMID: 12736311
- PMCID: PMC156033
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg351
The solution structure of an essential stem-loop of human telomerase RNA
Abstract
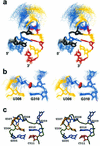
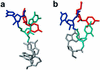
The ribonucleoprotein enzyme telomerase maintains chromosome ends in most eukaryotes and is critical for a cell's genetic stability and its proliferative viability. All telomerases contain a catalytic protein component homologous to viral reverse transcriptases (TERT) and an RNA (TR) that provides the template sequence as well as a scaffold for ribonucleoprotein assembly. Vertebrate telomerase RNAs have three essential domains: the template, activation and stability domains. Here we report the NMR structure of an essential RNA element derived from the human telomerase RNA activation domain. The sequence forms a stem-loop structure stabilized by a GU wobble pair formed by two of the five unpaired residues capping a short double helical region. The remaining three loop residues are in a well-defined conformation and form phosphate-base stacking interactions reminiscent of other RNA loop structures. Mutations of these unpaired nucleotides abolish enzymatic activity. The structure rationalizes a number of biochemical observations, and allows us to propose how the loop may function in the telomerase catalytic cycle. The pre-formed structure of the loop exposes the bases of these three essential nucleotides and positions them to interact with other RNA sequences within TR, with the reverse transcriptase or with the newly synthesized telomeric DNA strand. The functional role of this stem-loop appears to be conserved in even distantly related organisms such as yeast and ciliates.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The structure of an enzyme-activating fragment of human telomerase RNA.RNA. 2005 Apr;11(4):394-403. doi: 10.1261/rna.7222505. Epub 2005 Feb 9. RNA. 2005. PMID: 15703438 Free PMC article.
-
A critical stem-loop structure in the CR4-CR5 domain of mammalian telomerase RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 15;30(2):592-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.2.592. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11788723 Free PMC article.
-
The functional requirement of two structural domains within telomerase RNA emerged early in eukaryotes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Nov 16;44(20):9891-9901. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw605. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27378779 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary perspectives of telomerase RNA structure and function.RNA Biol. 2016 Aug 2;13(8):720-32. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1205768. Epub 2016 Jun 30. RNA Biol. 2016. PMID: 27359343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and function of telomerase RNA.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006 Jun;16(3):307-18. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.05.005. Epub 2006 May 18. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006. PMID: 16713250 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of pseudouridylation on the structure and activity of the catalytically essential P6.1 hairpin in human telomerase RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(19):6746-56. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq525. Epub 2010 Jun 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20554853 Free PMC article.
-
Refined secondary-structure models of the core of yeast and human telomerase RNAs directed by SHAPE.RNA. 2015 Feb;21(2):254-61. doi: 10.1261/rna.048959.114. Epub 2014 Dec 15. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25512567 Free PMC article.
-
A critical three-way junction is conserved in budding yeast and vertebrate telomerase RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(18):6280-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm713. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17855392 Free PMC article.
-
Thermodynamic analysis of 5' and 3' single- and 3' double-nucleotide overhangs neighboring wobble terminal base pairs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Oct;36(17):5652-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn525. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18765476 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for protein-RNA recognition in telomerase.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014 Jun;21(6):507-12. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2819. Epub 2014 May 4. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24793650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lingner J. and Cech,T.R. (1998) Telomerase and chromosome end maintanance. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 8, 226–232. - PubMed
-
- Lingner J., Hughes,T.R., Shevchenko,A., Mann,M., Lundblad,V. and Cech,T.R. (1997) Reverse transcriptase motifs in the catalytic subunit of telomerase. Science, 276, 561–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions

