Sigma 1 receptor-related neuroactive steroids modulate cocaine-induced reward
- PMID: 12736327
- PMCID: PMC6742197
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-09-03572.2003
Sigma 1 receptor-related neuroactive steroids modulate cocaine-induced reward
Abstract
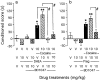
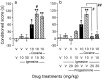
The sigma1 receptor is critically involved in the rewarding effect of cocaine, as measured using the conditioned place preference (CPP) procedure in mice. Neuroactive steroids exert rapid neuromodulatory effects in the brain by interacting with GABA(A), NMDA, and sigma1 receptors. At the sigma1 receptor level, 3beta-hydroxy-5-androsten-17-one [dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)] and 3beta-hydroxy-5-pregnen-20-one (pregnenolone) act as agonists, whereas 4-pregnene-3,20-dione (progesterone) is an efficient antagonist. The present study sought to investigate the action of neuroactive steroids in acquisition of cocaine-induced CPP in C57BL/6 mice. None of these steroids induced CPP alone. However, pretreatment with DHEA or pregnenolone (5-20 mg/kg, s.c.) during conditioning with cocaine (10 mg/kg, i.p.) increased the conditioned score. On the contrary, pretreatment with either progesterone (10 or 20 mg/kg, s.c.) or finasteride (25 mg/kg, twice a day), a 5alpha-reductase inhibitor, blocked acquisition of cocaine (20 mg/kg)-induced CPP. A crossed pharmacology was observed between steroids and sigma1 ligands. The sigma1 antagonist N-[2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-N-methyl-2-(dimethylamino)ethylamine blocked cocaine-induced CPP and its potentiation by DHEA or pregnenolone. Progesterone blocked cocaine-induced CPP and its potentiation by the sigma1 agonist igmesine. These results showed that neuroactive steroids play a role in cocaine-induced appetence, through their interaction with the sigma1 receptor. Therefore, neuroendocrine control of cocaine addiction may not involve solely glucocorticoids. The importance of neuroactive steroids as factors of individual vulnerability to drug addiction should, thus, be considered.
Figures


References
-
- Alonso G, Phan VL, Guillemain I, Saunier M, Legrand A, Anoal M, Maurice T. Immunocytochemical localization of the σ1 receptor in the adult rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 2000;97:155–170. - PubMed
-
- Ault DT, Radeff JM, Werling LL. Modulation of [3H] dopamine release from rat nucleus accumbens by neuropeptide Y may involve a sigma1-like receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998;284:553–560. - PubMed
-
- Barrot M, Vallée M, Gingras MA, Le Moal M, Mayo W, Piazza PV. The neurosteroid pregnenolone sulphate increases dopamine release and the dopaminergic response to morphine in the rat nucleus accumbens. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:3757–3760. - PubMed
-
- Baulieu EE. Steroid hormones in the brain: several mechanisms? In: Fuxe K, Gustafson JA, Wettenberg L, editors. Steroid hormone regulation of the brain. Pergamon; Oxford: 1981. pp. 3–14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
