Electrophysiological imaging of functional architecture in the cortical middle temporal visual area of Cebus apella monkey
- PMID: 12736358
- PMCID: PMC6742200
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-09-03881.2003
Electrophysiological imaging of functional architecture in the cortical middle temporal visual area of Cebus apella monkey
Abstract
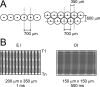
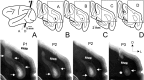
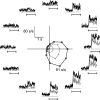
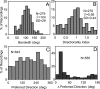
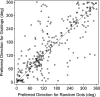
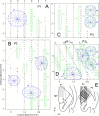
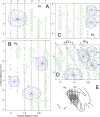
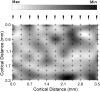
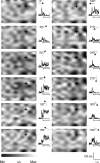
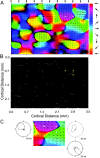
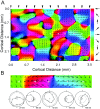
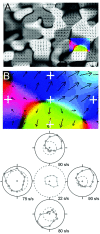
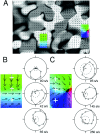
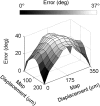
We studied the spatial organization of directionally selective neurons in the cortical middle temporal visual area (area MT) of the Cebus monkey. We recorded neuronal activity from multielectrode arrays as they were stepped through area MT. The set of recording sites in each array penetration described a plane parallel to the cortical layers. At each recording site, we determined the preferred direction of motion. Responses recorded at successive locations from the same electrode in the array revealed gradual changes in preferred direction, along with occasional directional reversals. Comparisons of responses from adjacent electrodes at successive locations enabled electrophysiological imaging of the two-dimensional pattern of preferred directions across the cortex. Our results demonstrate a systematic organization for directionality in area MT of the New World Cebus monkey, which is similar to that known to exist in the Old World macaque. In addition, our results provide electrophysiological confirmation of map features that have been documented in other cortical areas and primate species by optical imaging. Specifically, the tangential organization of directional selectivity is characterized by slow continuous changes in directional preference, as well as lines (fractures) and points (singularities) that fragment continuous regions into patches. These electrophysiological methods also allowed a direct investigation of neuronal selectivities that give rise to map features. In particular, our results suggest that inhibitory mechanisms may be involved in the generation of fractures and singularities.
Figures

References
-
- Albright TD. Direction and orientation selectivity of neurons in visual area MT of the macaque. J Neurophysiol. 1984;52:1106–1130. - PubMed
-
- Albright TD. Centrifugal directional bias in the middle temporal visual area (MT) of the macaque. Vis Neurosci. 1989;2:177–188. - PubMed
-
- Albright TD, Desimone R. Local precision of visuotopic organization in the middle temporal area (MT) of the macaque. Exp Brain Res. 1987;65:582–592. - PubMed
-
- Albright TD, Desimone R, Gross CG. Columnar organization of directionally selective cells in visual area MT of the macaque. J Neurophysiol. 1984;51:16–31. - PubMed
-
- Batschelet E. Circular statistics in biology. Academic; London: 1981.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
