Salicylate induces tinnitus through activation of cochlear NMDA receptors
- PMID: 12736364
- PMCID: PMC6742173
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-09-03944.2003
Salicylate induces tinnitus through activation of cochlear NMDA receptors
Abstract
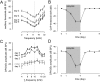
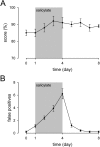
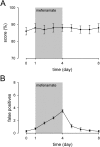
Salicylate, the active component of aspirin, is known to induce tinnitus. However, the site and the mechanism of generation of tinnitus induced by salicylate remains unclear. Here, we developed a behavioral procedure to measure tinnitus in rats. The behavioral model was based on an active avoidance paradigm in which rats had to display a motor task (i.e., to jump on a climbing pole when hearing a sound). Giving salicylate led to a decrease in the percentage of correct responses (score) and a drastic increase in the number of false positive responses (i.e., animals execute the motor task during a silent period). Presentation of the sound at a constant perceptive level prevents decrease of the score, leading to the proposal that score is related to hearing performance. In contrast, the increase of false positive responses remained unchanged. In fact, animals behaved as if they hear a sound, indicating that they are experiencing tinnitus. Mefenamate in place of salicylate also increased the number of false positive responses, suggesting that salicylate-induced tinnitus is related to an inhibition of cyclooxygenase. One physiological basis of salicylate ototoxicity is likely to originate from altered arachidonic acid metabolism. Because arachidonic acid potentiates NMDA receptor currents, we tested the involvement of cochlear NMDA receptors in the occurrence of tinnitus. Application of NMDA antagonists into the perilymphatic fluids of the cochlea blocked the increase in pole-jumping behavior induced by salicylate, suggesting that salicylate induces tinnitus through activation of cochlear NMDA receptors.
Figures



References
-
- Amann R, Peskar BA. Anti-inflammatory effects of aspirin and sodium salicyalte. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;447:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Basile AS, Huang JM, Xie C, Webster D, Berlin C, Skolnick P. N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonists limit aminoglycoside antibiotic-induced hearing loss. Nat Med. 1996;2:1338–1343. - PubMed
-
- Bauer CA, Brozoski TJ, Rojas R, Boley J, Wyder M. Behavioral model of chronic tinnitus in rats. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999;121:457–462. - PubMed
-
- Brownell WE, Bader CR, Bertrand D, de Ribaupierre Y. Evoked mechanical responses of isolated cochlear outer hair cells. Science. 1985;227:194–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
