Entamoeba moshkovskii infections in children, Bangladesh
- PMID: 12737742
- PMCID: PMC2972761
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0905.020548
Entamoeba moshkovskii infections in children, Bangladesh
Abstract
Entamoeba moshkovskii cysts are morphologically indistinguishable from those of the disease-causing species E. histolytica and the nonpathogenic E. dispar. Although sporadic cases of human infection with E. moshkovskii have been reported, the organism is considered primarily a free-living amoeba. No simple molecular detection tool is available for diagnosing E. moshkovskii infections. We used polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect E. moshkovskii directly in stool. We tested 109 stool specimens from preschool children in Bangladesh by PCR; 17 were positive for E. histolytica (15.6%) and 39 were positive for E. dispar (35.8%). In addition, we found that 23 (21.1%) were positive for E. moshkovskii infection, and 17 (73.9%) of these also carried E. histolytica or E. dispar. The high association of E. moshkovskii with E. histolytica and E. dispar may have obscured its identification in previous studies. The high prevalence found in this study suggests that humans may be a true host for this amoeba.
Figures
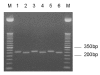

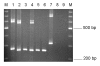
References
-
- Dreyer DA. Growth of a strain of Entamoeba histolytica at room temperature. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1961;19:393–6. - PubMed
-
- Entner N, Most H. Genetics of Entamoeba: characterization of two new parasitic strains that grow at room temperature (and at 37°C). J Protozool. 1965;12:10–3. - PubMed
-
- Richards CS, Goldman M, Cannon LT. Cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba histolytica-like strains at reduced temperature and behavior of the amebae in diluted media. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966;5:648–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
