The number of cells expressing dopamine D2 receptor mRNA in rat brain caudate putamen is higher in oestrus
- PMID: 12739622
- PMCID: PMC1571098
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00180.x
The number of cells expressing dopamine D2 receptor mRNA in rat brain caudate putamen is higher in oestrus
Abstract
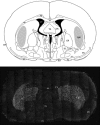
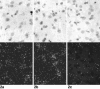
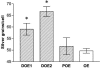
Dopamine D2 receptors (D2-Rs) in the central nervous system are involved in the control of locomotion, cognition, emotion and neuroendocrine secretion. The intensity of cellular responses to specific stimuli is dependent on the concentration of dopamine or its agonist, and the availability, as well as the concentration, of all the other components of the signalling pathway in the cell, including the receptors. Many factors can influence the level of mRNA encoding the receptors. In order to study the changes in the level of expression of the D2-R mRNA in the brain of female rats at different stages of the oestrous cycle, we used a quantitative in situ hybridization technique. Four groups of animals were analysed: rats in prooestrus (POE), oestrus (OE), dioestrus 1 (DOE1) and dioestrus 2 (DOE2). A 35S-labelled riboprobe was transcribed in vitro from the 1.5-kb D2-R cDNA. The caudate putamen of the rats, which shows the highest level of expression of D2-R mRNA in the brain, was examined. The number of silver grains per cell, representing hybridization of riboprobe, and the number of cells expressing the D2-R mRNA, were counted with the computer-assisted image analysis system Lucia-M. Our results show that the expression of the D2-R mRNA in the lateral striatum varies during the oestrous cycle, with the highest expression measured during DOE2. The number of cells expressing the D2-R mRNA also changes during the different phases, with the highest number being detected in OE. This indicates that during OE more cells transcribe the D2-R mRNA. The results suggest that the variations in the concentration of the D2-R mRNA in the caudate putamen of the rat brain at different stages of the reproductive cycle are caused by the combination of variable expression of the mRNA per cell and different number of the cells that express the mRNA.
Figures
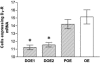
Similar articles
-
Effect of raclopride on dopamine D2 receptor mRNA expression in rat brain.Neuroscience. 1992;47(4):771-9. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90028-z. Neuroscience. 1992. PMID: 1533704
-
Heterogeneous distribution of dopamine D2 receptor mRNA in the rat striatum: a quantitative analysis with in situ hybridization histochemistry.Anat Rec. 1991 Dec;231(4):548-58. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092310416. Anat Rec. 1991. PMID: 1838906
-
Dopamine D2 receptor mRNA in the pituitary during the oestrous cycle, pregnancy and lactation in the rat.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1993 Sep;95(1-2):121-8. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(93)90037-k. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1993. PMID: 8243802
-
The distribution of dopamine D2 receptor heteronuclear RNA (hnRNA) in the rat brain.J Chem Neuroanat. 1993 Nov-Dec;6(6):363-73. doi: 10.1016/0891-0618(93)90011-r. J Chem Neuroanat. 1993. PMID: 8142073
-
Dopamine D2 receptor mRNA measured in serial sections of the rat anterior pituitary.Pflugers Arch. 2001;442(6 Suppl 1):R209-10. doi: 10.1007/s004240100028. Pflugers Arch. 2001. PMID: 11678343
Cited by
-
Steroids-dopamine interactions in the pathophysiology and treatment of CNS disorders.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2010 Jun;16(3):e43-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00163.x. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2010. PMID: 20557567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estradiol metabolism by gut microbiota in women's depression pathogenesis: inspiration from nature.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Jan 28;16:1505991. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1505991. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39935532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced sensitivity to cocaine effects and changes in mesocorticolimbic dopamine receptors in adolescent sexually active female rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025 Apr;242(4):817-834. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06741-3. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025. PMID: 39729197
-
Estradiol Receptors Inhibit Long-Term Potentiation in the Dorsomedial Striatum.eNeuro. 2023 Aug 3;10(8):ENEURO.0071-23.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0071-23.2023. Print 2023 Aug. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 37487741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bazzett TJ, Becker JB. Sex differences in the rapid and acute effects of estrogen on striatal D2 dopamine receptor binding. Brain Res. 1994;637:163–172. - PubMed
-
- Becker JB, Rudick CN. Rapid effects of estrogen or progesterone on the amphetamine-induced increase in striatal dopamine are enhanced by estrogen priming: a microdialysis study. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1999;64:53–57. - PubMed
-
- Di Paolo T, Bedard PJ, Dupont A, Poyet P, Labrie F. Effects of estradiol on intact and denervated striatal dopamine receptors and on dopamine levels: a biochemical and behavioral study. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1982;60:350–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

