Molecular responses to hypoxia in tumor cells
- PMID: 12740039
- PMCID: PMC155638
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-2-23
Molecular responses to hypoxia in tumor cells
Abstract
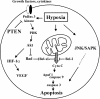
Highly aggressive, rapidly growing tumors are exposed to hypoxia or even anoxia which occurs as a consequence of inadequate blood supply. Both hypoxia and consecutive hypoxia/reoxygenation exert a variety of influences on tumor cell biology. Among these are activation of certain signal transduction pathways and gene regulatory mechanisms, induction of selection processes for gene mutations, tumor cell apoptosis and tumor angiogenesis. Most of these mechanisms contribute to tumor progression. Therefore, tissue hypoxia has been regarded as a central factor for tumor aggressiveness and metastasis. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge about the molecular mechanisms induced by tumor cell hypoxia with a special emphasis on intracellular signal transduction, gene regulation, angiogenesis and apoptosis. Interfering with these pathways might open perspectives for future innovative treatment of highly aggressive metastasizing tumors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Overexpression of Ref-1 inhibits hypoxia and tumor necrosis factor-induced endothelial cell apoptosis through nuclear factor-kappab-independent and -dependent pathways.Circ Res. 2001 Jun 22;88(12):1247-53. doi: 10.1161/hh1201.091796. Circ Res. 2001. PMID: 11420300
-
Gender-related differences in basal and hypoxia-induced activation of signal transduction pathways controlling cell cycle progression and apoptosis, in cardiac fibroblasts.Endocrine. 2002 Jul;18(2):137-45. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:18:2:137. Endocrine. 2002. PMID: 12374461
-
The genomic response of tumor cells to hypoxia and reoxygenation. Differential activation of transcription factors AP-1 and NF-kappa B.Eur J Biochem. 1995 Dec 1;234(2):632-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.632_b.x. Eur J Biochem. 1995. PMID: 8536713
-
Tumor cell hypoxia and the hypoxia-response signaling system as a target for prostate cancer therapy.Curr Drug Targets. 2003 Apr;4(3):191-6. doi: 10.2174/1389450033491136. Curr Drug Targets. 2003. PMID: 12643469 Review.
-
MAP kinases and hypoxia in the control of VEGF expression.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2000;19(1-2):139-45. doi: 10.1023/a:1026506011458. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2000. PMID: 11191053 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of MDR1, HIF-1α and MRP1 in sacral chordoma and chordoma cell line CM-319.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Dec 8;29(1):158. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-158. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21143841 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of PLD2 in hypoxia-induced stemness and therapy resistance in ovarian tumors.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Feb 26;43(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-02988-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38403587 Free PMC article.
-
Crypt dynamics and colorectal cancer: advances in mathematical modelling.Cell Prolif. 2006 Jun;39(3):157-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2006.00378.x. Cell Prolif. 2006. PMID: 16671995 Free PMC article.
-
Morning breathing exercises prolong lifespan by improving hyperventilation in people living with respiratory cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jan;96(2):e5838. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005838. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28079815 Free PMC article.
-
Cycling hypoxia induces chemoresistance through the activation of reactive oxygen species-mediated B-cell lymphoma extra-long pathway in glioblastoma multiforme.J Transl Med. 2015 Dec 28;13:389. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0758-8. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26711814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Folkman J, Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:10931–10934. - PubMed
-
- Helmlinger G, Yuan F, Dellian M, Jain RK. Interstitial pH and pO2 gradients in solid tumors in vivo: High resolution measurements reveal a lack of correlation. Nat Med. 1997;3:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Coleman CN, Mitchell JB, Camphausen K. Tumor hypoxia: chicken, egg, or a piece of the farm? J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:610–615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

