Child-Pugh versus MELD score in predicting survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
- PMID: 12740346
- PMCID: PMC1773665
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.52.6.879
Child-Pugh versus MELD score in predicting survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
Abstract
Background: In patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS), prognostic scores may identify those with a poor prognosis or even those with a clear survival benefit. The Child-Pugh score (CPS) is well established but several drawbacks have led to development of the model of end stage liver disease (MELD).
Aim: The aim of the study was to compare the predictive power of CPS and MELD, to validate the original MELD formula, and to assess the predictive value of the determinants used in the two prognostic scores outside of a study setting.
Patients: A total of 501 patients underwent elective TIPS placement and 475 patients fulfilled the inclusion criteria.
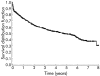
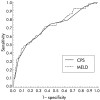
Methods: Data of all patients undergoing elective TIPS in one university hospital and four community hospitals in Vienna, Austria, between 1991 and 2001, were analysed retrospectively. The main statistical tests were Cox proportional hazards regression model, the log rank test, Kaplan-Meier analysis, and concordance c statistics.
Results: Median follow up was 5.2 years and median survival was 4.6 years. During follow up, 230 patients died, 75 within three months after TIPS placement. In stepwise proportional hazards analyses, independent predictors of death were creatinine level, bilirubin level, age, and refractory ascites. MELD was better in predicting survival in a stepwise Cox model but both scores were equally predictive in c statistics for one month, three month, and one year survival. Renal function was the strongest independent predictor of survival.
Conclusions: Although MELD was the primary predictor of overall survival in multivariate analysis, c statistics showed that both scores can be used for patients undergoing TIPS with equal accuracy. For assessing prognosis in patients undergoing TIPS implantation, there seems little reason to replace the well established Child-Pugh score.
Figures
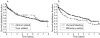
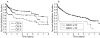
References
-
- Rossle M, Haag K, Ochs A, et al. The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt procedure for variceal bleeding. N Engl J Med 1994;330:165–71. - PubMed
-
- Rossle M, Ochs A, Gulberg V, et al. A comparison of paracentesis and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting in patients with ascites. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1701–7. - PubMed
-
- Sanyal AJ. The use and misuse of transjugular intrahepatic portasystemic shunts. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2000;2:61–71. - PubMed
-
- Ochs A, Rössle M, Haag K, et al. The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt procedure for refractory ascites (published erratum appears in N Engl J Med 1995;332:1587). N Engl J Med 1995;332:1192–7. - PubMed
-
- Rössle M, Deibert P, Haag K, et al. Randomised trial of transjugular-intrahepatic-portosystemic shunt versus endoscopy plus propranolol for prevention of variceal rebleeding. Lancet 1997;349:1043–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
