M phase phosphoprotein 1 is a human plus-end-directed kinesin-related protein required for cytokinesis
- PMID: 12740395
- PMCID: PMC2652640
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M304522200
M phase phosphoprotein 1 is a human plus-end-directed kinesin-related protein required for cytokinesis
Abstract
The human M phase phosphoprotein 1 (MPP1), previously identified through a screening of a subset of proteins specifically phosphorylated at the G2/M transition (Matsumoto-Taniura, N., Pirollet, F., Monroe, R., Gerace, L., and Westendorf, J. M. (1996) Mol. Biol. Cell 7, 1455-1469), is characterized as a plus-end-directed kinesin-related protein. Recombinant MPP1 exhibits in vitro microtubule-binding and microtubule-bundling properties as well as microtubule-stimulated ATPase activity. In gliding experiments using polarity-marked microtubules, MPP1 is a slow molecular motor that moves toward the microtubule plus-end at a 0.07 microm/s speed. In cycling cells, MPP1 localizes mainly to the nuclei in interphase. During mitosis, MPP1 is diffuse throughout the cytoplasm in metaphase and subsequently localizes to the midzone to further concentrate on the midbody. MPP1 suppression by RNA interference induces failure of cell division late in cytokinesis. We conclude that MPP1 is a new mitotic molecular motor required for completion of cytokinesis.
Figures


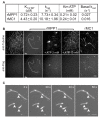
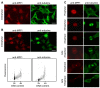

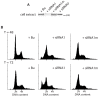
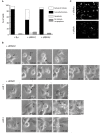
 , ★) show daughter cells from the same mitotic cell. md indicates a mitotic defect, bin, a binucleated cell and a, an apoptotic cell. Time shown is in hours and min. C. MPP1 expression in siRNA-transfected cells. Indirect immunofluorescence of HCT116 cells stained with the anti-MPP1 antibody, 24 h after transfection with the indicated duplexes. The pattern obtained after siRNAU transfection is similar to the one after mockand siRNAi1m transfection (data not shown). As the cells were stained and the pictures acquired and processed under exactly the same conditions, this indicates that the level of transfection with siRNAi1 was very high and we can assume that the cells that we looked at in Fig 7B are actually transfected.
, ★) show daughter cells from the same mitotic cell. md indicates a mitotic defect, bin, a binucleated cell and a, an apoptotic cell. Time shown is in hours and min. C. MPP1 expression in siRNA-transfected cells. Indirect immunofluorescence of HCT116 cells stained with the anti-MPP1 antibody, 24 h after transfection with the indicated duplexes. The pattern obtained after siRNAU transfection is similar to the one after mockand siRNAi1m transfection (data not shown). As the cells were stained and the pictures acquired and processed under exactly the same conditions, this indicates that the level of transfection with siRNAi1 was very high and we can assume that the cells that we looked at in Fig 7B are actually transfected.References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

