Gamma-secretase is a membrane protein complex comprised of presenilin, nicastrin, Aph-1, and Pen-2
- PMID: 12740439
- PMCID: PMC164455
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1037392100
Gamma-secretase is a membrane protein complex comprised of presenilin, nicastrin, Aph-1, and Pen-2
Abstract
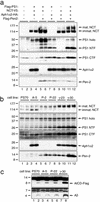
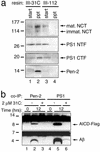
gamma-Secretase catalyzes the intramembrane proteolysis of Notch, beta-amyloid precursor protein, and other substrates as part of a new signaling paradigm and as a key step in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. This unusual protease has eluded identification, though evidence suggests that the presenilin heterodimer comprises the catalytic site and that a highly glycosylated form of nicastrin associates with it. The formation of presenilin heterodimers from the holoprotein is tightly gated by unknown limiting cellular factors. Here we show that Aph-1 and Pen-2, two recently identified membrane proteins genetically linked to gamma-secretase, associate directly with presenilin and nicastrin in the active protease complex. Coexpression of all four proteins leads to marked increases in presenilin heterodimers, full glycosylation of nicastrin, and enhanced gamma-secretase activity. These findings suggest that the four membrane proteins comprise the limiting components of gamma-secretase and coassemble to form the active enzyme in mammalian cells.
Figures


References
-
- Brown, M. S., Ye, J., Rawson, R. B. & Goldstein, J. L. (2000) Cell 100, 391–398. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe, M. S. & Selkoe, D. J. (2002) Science 296, 2156–2157. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe, D. J. (2001) Physiol. Rev. 81, 741–766. - PubMed
-
- Thinakaran, G., Borchelt, D. R., Lee, M. K., Slunt, H. H., Spitzer, L., Kim, G., Ratovitsky, T., Davenport, F., Nordstedt, C., Seeger, M., et al. (1996) Neuron 17, 181–190. - PubMed
-
- Li, Y. M., Xu, M., Lai, M. T., Huang, Q., Castro, J. L., DiMuzio-Mower, J., Harrison, T., Lellis, C., Nadin, A., Neduvelil, J. G., et al. (2000) Nature 405, 689–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

