Disruption of the estrogen receptor beta gene in mice causes myeloproliferative disease resembling chronic myeloid leukemia with lymphoid blast crisis
- PMID: 12740446
- PMCID: PMC164509
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0731830100
Disruption of the estrogen receptor beta gene in mice causes myeloproliferative disease resembling chronic myeloid leukemia with lymphoid blast crisis
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 23;103(21):8298
Abstract
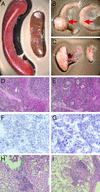
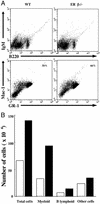
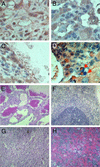
Proliferation of pluripotent, bone marrow stem cells, which develop to lymphoid and myeloid progenitors, is negatively regulated by estrogen. Although in estrogen deficiency and in estrogen receptor knockout mice there is significant alteration in bone marrow hematopoiesis, the effects of aging on estrogen receptor deficiencies in mice have not been investigated yet. In this study we show that by 1.5 years of age, estrogen receptor beta knockout (ERbeta-/-) mice develop pronounced splenomegaly that is much more severe in females than in males. Further characterization of these mice revealed myelogenous hyperplasia in bone marrow, an increase in the number of granulocytes and B lymphocytes in blood, lymphadenopathy, and infiltration of leukocytes in the liver and lung. Analysis by flow cytometry of the bone marrow cells revealed that the percentage and total number of Gr-1hi/Mac-1hi-positive granulocytes were increased by 15-30% and 100%, respectively. The numbers of B cells in the bone marrow and spleen were significantly higher in ERbeta-/- mice than in WT littermates. Some of the ERbeta-/- mice also had a severe lymphoproliferative phenotype. Thus the absence of ERbeta results in a myeloproliferative disease resembling human chronic myeloid leukemia with lymphoid blast crisis. Our results indicate a previously unknown role for ERbeta in regulating the differentiation of pluripotent hematopoietic progenitor cells and suggest that the ERbeta-/- mouse is a potential model for myeloid and lymphoid leukemia. Furthermore, we suggest that ERbeta agonists might have clinical value in the treatment of leukemia.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Efficient and rapid induction of a chronic myelogenous leukemia-like myeloproliferative disease in mice receiving P210 bcr/abl-transduced bone marrow.Blood. 1998 Nov 15;92(10):3780-92. Blood. 1998. PMID: 9808572
-
The Src homology-2 protein Shb modulates focal adhesion kinase signaling in a BCR-ABL myeloproliferative disorder causing accelerated progression of disease.J Hematol Oncol. 2014 Jun 21;7:45. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-7-45. J Hematol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24952416 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of interferon consensus sequence binding protein (ICSBP) is downregulated in Bcr-Abl-induced murine chronic myelogenous leukemia-like disease, and forced coexpression of ICSBP inhibits Bcr-Abl-induced myeloproliferative disorder.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Feb;20(4):1149-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.4.1149-1161.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10648600 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloproliferative disorders. Classification and diagnostic features with special emphasis on chronic myelogenous leukemia and agnogenic myeloid metaplasia.Clin Lab Med. 1990 Dec;10(4):825-38. Clin Lab Med. 1990. PMID: 2272176 Review.
-
Pathogenetic mechanisms in chronic myeloproliferative disorders: polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, agnogenic myeloid metaplasia, and chronic myelogenous leukemia.Semin Hematol. 1999 Jan;36(1 Suppl 2):3-8. Semin Hematol. 1999. PMID: 9930550 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Estrogen Receptor Beta in a Phase 2 Study of High-Dose Estradiol in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Wisconsin Oncology Network Study.Clin Breast Cancer. 2016 Aug;16(4):256-61. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Clin Breast Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27133732 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Estrogen treatment induces MLL aberrations in human lymphoblastoid cells.Leuk Res. 2009 Oct;33(10):1400-4. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2009.01.023. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Leuk Res. 2009. PMID: 19264358 Free PMC article.
-
Delay of postnatal maturation sensitizes the mouse prostate to testosterone-induced pronounced hyperplasia: protective role of estrogen receptor-beta.Am J Pathol. 2007 Sep;171(3):1013-22. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060979. Epub 2007 Jul 19. Am J Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17640960 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen Receptor Beta (ERβ): A Ligand Activated Tumor Suppressor.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 23;10:587386. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.587386. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33194742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen promotes megakaryocyte polyploidization via estrogen receptor beta-mediated transcription of GATA1.Leukemia. 2017 Apr;31(4):945-956. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.285. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Leukemia. 2017. PMID: 27748371
References
-
- Whitacre, C. C. (2001) Nat. Immunol. 2, 777–780. - PubMed
-
- Zhang, J., Pugh, T. D., Stebler, B., Ershler, W. B. & Keller, E. T. (1998) Calcif. Tissue Int. 62, 219–226. - PubMed
-
- Erben, R. G., Raith, S., Eberle, J. & Stangassinger, M. (1998) Am. J. Physiol. 274, E476–E483. - PubMed
-
- Jilka, R. L., Passeri, G., Girasole, G., Cooper, S., Abrams, J., Broxmeyer, H. & Manolagas, S. C. (1995) Exp. Hematol. (Charlottesville, Va) 23, 500–506. - PubMed
-
- Jilka, R. L., Hangoc, G., Girasole, G., Passeri, G., Williams, D. C., Abrams, J. S., Boyce, B., Boxmeyer, H. & Manolagas, S. C. (1992) Science 257, 88–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

