Regulation of Smad signaling through a differential recruitment of coactivators and corepressors by ZEB proteins
- PMID: 12743039
- PMCID: PMC155984
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg226
Regulation of Smad signaling through a differential recruitment of coactivators and corepressors by ZEB proteins
Abstract
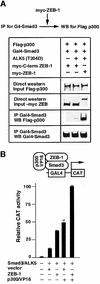
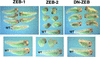
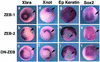
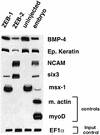
Balancing signals derived from the TGFbeta family is crucial for regulating cell proliferation and differentiation, and in establishing the embryonic axis during development. TGFbeta/BMP signaling leads to the activation and nuclear translocation of Smad proteins, which activate transcription of specific target genes by recruiting P/CAF and p300. The two members of the ZEB family of zinc finger factors (ZEB-1/deltaEF1 and ZEB-2/SIP1) regulate TGFbeta/BMP signaling in opposite ways: ZEB-1/deltaEF1 synergizes with Smad-mediated transcriptional activation, while ZEB-2/SIP1 represses it. Here we report that these antagonistic effects by the ZEB proteins arise from the differential recruitment of transcriptional coactivators (p300 and P/CAF) and corepressors (CtBP) to the Smads. Thus, while ZEB-1/deltaEF1 binds to p300 and promotes the formation of a p300-Smad transcriptional complex, ZEB-2/SIP1 acts as a repressor by recruiting CtBP. This model of regulation by ZEB proteins also functions in vivo, where they have opposing effects on the regulation of TGFbeta family-dependent genes during Xenopus development.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Opposing functions of ZEB proteins in the regulation of the TGFbeta/BMP signaling pathway.EMBO J. 2003 May 15;22(10):2443-52. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg225. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12743038 Free PMC article.
-
SIP1 (Smad interacting protein 1) and deltaEF1 (delta-crystallin enhancer binding factor) are structurally similar transcriptional repressors.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A Suppl 1(Pt 1):S40-7. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11263664 Review.
-
New mode of DNA binding of multi-zinc finger transcription factors: deltaEF1 family members bind with two hands to two target sites.EMBO J. 1999 Sep 15;18(18):5073-84. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.18.5073. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 10487759 Free PMC article.
-
SIP1, a novel zinc finger/homeodomain repressor, interacts with Smad proteins and binds to 5'-CACCT sequences in candidate target genes.J Biol Chem. 1999 Jul 16;274(29):20489-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.29.20489. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10400677
-
Transforming growth factor beta signalling in vitro and in vivo: activin ligand-receptor interaction, Smad5 in vasculogenesis, and repression of target genes by the deltaEF1/ZEB-related SIP1 in the vertebrate embryo.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001 Jun 30;180(1-2):13-24. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00505-6. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11451567 Review.
Cited by
-
EMT-activating transcription factors in cancer: beyond EMT and tumor invasiveness.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Oct;69(20):3429-56. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1122-2. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22945800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-Translational Modification of ZEB Family Members in Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 1;23(23):15127. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315127. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) is required for neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 14;293(50):19317-19329. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005498. Epub 2018 Oct 18. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30337365 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of ZEB1 Function and Molecular Associations in Tumor Progression and Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 7;14(8):1864. doi: 10.3390/cancers14081864. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic and proteomic profiling I: leiomyomas in African Americans and Caucasians.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2007 Aug 23;5:34. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-5-34. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17716379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannister A.J. and Kouzarides,T. (1996) The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature, 384, 641–643. - PubMed
-
- Barlev N.A., Liu,L., Chehab,N.H., Mansfield,K., Harris,K.G., Halazonetis,T.D. and Berger,S.L. (2001) Acetylation of p53 activates transcription through recruitment of coactivators/histone acetyltransferases. Mol. Cell, 8, 1243–1254. - PubMed
-
- Candia A.F., Watabe,T., Hawley,S.H., Onichtchouk,D., Zhang,Y., Derynck,R., Niehrs,C. and Cho,K.W. (1997) Cellular interpretation of multiple TGF-β signals: intracellular antagonism between activin/BVg1 and BMP-2/4 signaling mediated by Smads. Development, 124, 4467–4480. - PubMed
-
- Chakravarti D., Ogryzko,V., Kao,H.Y., Nash,A., Chen,H., Nakatani,Y. and Evans,R,M. (1999) A viral mechanism for inhibition of p300 and PCAF acetyltransferase activity. Cell, 96, 393–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

