Pore structure influences gating properties of the T-type Ca2+ channel alpha1G
- PMID: 12743166
- PMCID: PMC2217349
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200308794
Pore structure influences gating properties of the T-type Ca2+ channel alpha1G
Abstract
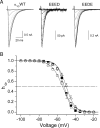
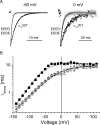
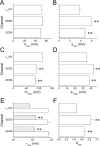
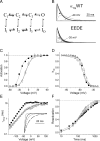
The selectivity filter of all known T-type Ca2+ channels is built by an arrangement of two glutamate and two aspartate residues, each one located in the P-loops of domains I-IV of the alpha1 subunit (EEDD locus). The mutations of the aspartate residues to glutamate induce changes in the conduction properties, enhance Cd2+ and proton affinities, and modify the activation curve of the channel. Here we further analyze the role of the selectivity filter in the gating mechanisms of T-type channels by comparing the kinetic properties of the alpha1G subunit (CaV3.1) to those of pore mutants containing aspartate-to-glutamate substitution in domains III (EEED) or IV (EEDE). The change of the extracellular pH induced similar effects on the activation properties of alpha1G and both pore mutants, indicating that the larger affinity of the mutant channels for protons is not the cause of the gating modifications. Both mutants showed alterations in several gating properties with respect to alpha1G, i.e., faster macroscopic inactivation in the voltage range from -10 to 50 mV, positive voltage shift and decrease in the voltage sensitivity of the time constants of activation and deactivation, decrease of the voltage sensitivity of the steady-state inactivation, and faster recovery from inactivation for long repolarization periods. Kinetic modeling suggests that aspartate-to-glutamate mutations in the EEDD locus of alpha1G modify the movement of the gating charges and alter the rate of several gating transitions. These changes are independent of the alterations of the selectivity properties and channel protonation.
Figures



References
-
- Alvarez, J.L., A. Artiles, K. Talavera, and G. Vassort. 2000. Modulation of voltage-dependent facilitation of the T-type calcium current by sodium ion in isolated frog atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 441:39–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

