Host range of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in cultured cells
- PMID: 12743304
- PMCID: PMC155009
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.11.6474-6481.2003
Host range of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in cultured cells
Abstract
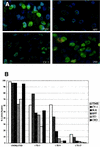
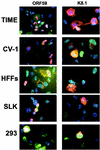
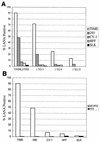
Difficulties in efficiently propagating Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) in culture have generated the impression that the virus displays a narrow host range. Here we show that, contrary to expectation, KSHV can establish latent infection in many adherent cell lines, including human and nonhuman cells of epithelial, endothelial, and mesenchymal origin. (Paradoxically, the only lines in which we have not observed successful latent infection are cultured lymphoma cell lines.) In most latently infected lines, spontaneous lytic replication is rare and (with only two exceptions) is not efficiently induced by phorbol ester treatment-a result that explains the failure of most earlier studies to observe efficient serial transfer of infection. However, ectopic expression of the KSHV lytic switch protein RTA from an adenoviral vector leads to the prompt induction of lytic replication in all latently infected lines, with the production of infectious KSHV virions. These results indicate (i) that the host cell receptor(s) and entry machinery for KSHV are widely distributed on cultured adherent cells, (ii) that latency is the default pathway of infection, and (iii) that blocks to lytic induction are frequent and largely reside at or upstream of the expression of KSHV RTA.
Figures
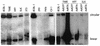
References
-
- Akula, S. M., N. P. Pramod, F. Z. Wang, and B. Chandran. 2002. Integrin alpha3beta1 (CD 49c/29) is a cellular receptor for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) entry into the target cells. Cell 108:407-419. - PubMed
-
- Blackbourn, D. J., E. Lennette, B. Klencke, A. Moses, B. Chandran, M. Weinstein, R. G. Glogau, M. H. Witte, D. L. Way, T. Kutzkey, B. Herndier, and J. A. Levy. 2000. The restricted cellular host range of human herpesvirus 8. AIDS 14:1123-1133. - PubMed
-
- Boshoff, C., T. F. Schulz, M. M. Kennedy, A. K. Graham, C. Fisher, A. Thomas, J. O. McGee, R. A. Weiss, and J. J. O'Leary. 1995. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infects endothelial and spindle cells. Nat. Med. 1:1274-1278. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman, E., Y. Chang, P. S. Moore, J. W. Said, and D. M. Knowles. 1995. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 332:1186-1191. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

