A novel family in Medicago truncatula consisting of more than 300 nodule-specific genes coding for small, secreted polypeptides with conserved cysteine motifs
- PMID: 12746522
- PMCID: PMC166962
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.102.018192
A novel family in Medicago truncatula consisting of more than 300 nodule-specific genes coding for small, secreted polypeptides with conserved cysteine motifs
Abstract
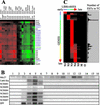
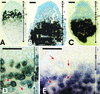
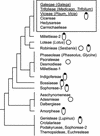
Transcriptome analysis of Medicago truncatula nodules has led to the discovery of a gene family named NCR (nodule-specific cysteine rich) with more than 300 members. The encoded polypeptides were short (60-90 amino acids), carried a conserved signal peptide, and, except for a conserved cysteine motif, displayed otherwise extensive sequence divergence. Family members were found in pea (Pisum sativum), broad bean (Vicia faba), white clover (Trifolium repens), and Galega orientalis but not in other plants, including other legumes, suggesting that the family might be specific for galegoid legumes forming indeterminate nodules. Gene expression of all family members was restricted to nodules except for two, also expressed in mycorrhizal roots. NCR genes exhibited distinct temporal and spatial expression patterns in nodules and, thus, were coupled to different stages of development. The signal peptide targeted the polypeptides in the secretory pathway, as shown by green fluorescent protein fusions expressed in onion (Allium cepa) epidermal cells. Coregulation of certain NCR genes with genes coding for a potentially secreted calmodulin-like protein and for a signal peptide peptidase suggests a concerted action in nodule development. Potential functions of the NCR polypeptides in cell-to-cell signaling and creation of a defense system are discussed.
Figures




References
-
- Bergelson J, Kreitman M, Stahl EA, Tian D. Evolutionary dynamics of plant R-genes. Science. 2001;292:2281–2285. - PubMed
-
- Bontems F, Roumestand C, Gilquin B, Menez A, Toma F. Refined structure of charybdotoxin: common motifs in scorpion toxins and insect defensins. Science. 1991;254:1521–1523. - PubMed
-
- Buck L, Axel R. A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: a molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell. 1991;65:175–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

