Treatment of acute intracranial vertebrobasilar dissection with angioplasty and stent placement: report of two cases
- PMID: 12748108
- PMCID: PMC7975807
Treatment of acute intracranial vertebrobasilar dissection with angioplasty and stent placement: report of two cases
Abstract
Acute vertebrobasilar dissection may cause subarachnoid hemorrhage by rupturing through the adventia or cerebral infarct by progressive occlusion of the true lumen. Recent reports on the endovascular management of this condition have focused on treatment of pseudoaneurysms. We report two cases where angioplasty or stent placement was successfully used to improve compromised blood flow secondary to vertebrobasilar dissection.
Figures
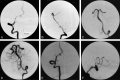


References
-
- Hosoya T, Adachi M, Yamaguchi K, et al. Clinical and neuroradiological features of intracranial vertebrobasilar artery dissection.Stroke 1999;30:1083–1090 - PubMed
-
- Mizutani T, Aruga T, Kirino T, et al. Recurrent subarachnoid hemorrhage from untreated ruptured vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysms.Neurosurgery 1995;36:905–911; discussion 912–913 - PubMed
-
- Malek AM, Higashida RT, Halbach VV, et al. Tandem intracranial stent deployment for treatment of an iatrogenic, flow-limiting, basilar artery dissection: technical case report.Neurosurgery 1999;45:919–924 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
