Inactivation of dual-specificity phosphatases is involved in the regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by heat shock and hsp72
- PMID: 12748284
- PMCID: PMC155207
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.11.3813-3824.2003
Inactivation of dual-specificity phosphatases is involved in the regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by heat shock and hsp72
Abstract
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) and ERK2 (ERK1/2) dramatically enhance survival of cells exposed to heat shock. Using Cos-7 cells and primary human fibroblasts (IMR90 cells), we demonstrated that heat shock activates ERKs via two distinct mechanisms: stimulation of the ERK-activating kinases, MEK1/2, and inhibition of ERK dephosphorylation. Under milder heat shock conditions, activation of ERKs proceeded mainly through stimulation of MEK1/2, whereas under more severe heat shock MEK1/2 could no longer be activated and the inhibition of ERK phosphatases became critical. In Cos-7 cells, nontoxic heat shock caused rapid inactivation of the major ERK phosphatase, MKP-3, by promoting its aggregation, so that in cells exposed to 45 degrees C for 20 min, 90% of MKP-3 became insoluble. MKP-3 aggregation was reversible and, 1 h after heat shock, MKP-3 partially resolubilized. The redistribution of MKP-3 correlated with an increased rate of ERK dephosphorylation. Similar heat-induced aggregation, followed by partial resolubilization, was found with a distinct dual-specificity phosphatase MKP-1 but not with MKP-2. Therefore, MKP-3 and MKP-1 appeared to be critical heat-labile phosphatases involved in the activation of ERKs by heat shock. Expression of the major heat shock protein Hsp72 inhibited activation of MEK1/2 and prevented inactivation of MKP-3 and MKP-1. Hsp72DeltaEEVD mutant lacking a chaperone activity was unable to protect MKP-3 from heat inactivation but interfered with MEK1/2 activation similar to normal Hsp72. Hence, Hsp72 suppressed ERK activation by both protecting dual-specificity phosphatases, which was dependent on the chaperone activity, and suppressing MEK1/2, which was independent of the chaperone activity.
Figures


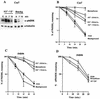
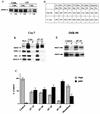


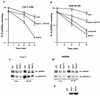
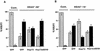
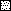 , supernatant; ▪, pellet.
, supernatant; ▪, pellet.
 , supernatant; ▪, pellet.
, supernatant; ▪, pellet.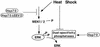
Similar articles
-
Preheating accelerates mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase inactivation post-heat shock via a heat shock protein 70-mediated increase in phosphorylated MAP kinase phosphatase-1.J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 1;280(13):13179-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410059200. Epub 2005 Jan 26. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15677475
-
Compartment-specific regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) by ERK-dependent and non-ERK-dependent inductions of MAPK phosphatase (MKP)-3 and MKP-1 in differentiating P19 cells.Biochem J. 2000 Dec 15;352 Pt 3(Pt 3):701-8. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 11104676 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback regulation of Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP) kinase kinases 1 and 2 by MAP kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1).J Biol Chem. 1998 Jan 16;273(3):1788-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.3.1788. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9430728
-
Regulation of innate immune response by MAP kinase phosphatase-1.Cell Signal. 2007 Jul;19(7):1372-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.03.013. Epub 2007 Apr 20. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 17512700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual-specificity phosphatases: critical regulators with diverse cellular targets.Biochem J. 2009 Mar 15;418(3):475-89. doi: 10.1042/bj20082234. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19228121 Review.
Cited by
-
Heat shock affects trafficking of DAX-1 by inducing its rapid and reversible cytoplasmic localization.Endocrine. 2005 Nov;28(2):137-44. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:28:2:137. Endocrine. 2005. PMID: 16388085
-
The complex function of hsp70 in metastatic cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2013 Dec 20;6(1):42-66. doi: 10.3390/cancers6010042. Cancers (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24362507 Free PMC article.
-
HSP72 protects against obesity-induced insulin resistance.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Feb 5;105(5):1739-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705799105. Epub 2008 Jan 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18223156 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer cell responses to Hsp70 inhibitor JG-98: Comparison with Hsp90 inhibitors and finding synergistic drug combinations.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 14;8(1):3010. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14900-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29445088 Free PMC article.
-
VRK3-mediated nuclear localization of HSP70 prevents glutamate excitotoxicity-induced apoptosis and Aβ accumulation via enhancement of ERK phosphatase VHR activity.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 12;6:38452. doi: 10.1038/srep38452. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27941812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi, D. R., N. Gomez, G. Moorhead, T. Lewis, S. M. Keyse, and P. Cohen. 1995. Inactivation of p42 MAP kinase by protein phosphatase 2A and a protein tyrosine phosphatase, but not CL100, in various cell lines. Curr. Biol. 5:283-295. - PubMed
-
- Camps, M., A. Nichols, C. Gillieron, B. Antonsson, M. Muda, C. Chabert, U. Boschert, and S. Arkinstall. 1998. Catalytic activation of the phosphatase MKP-3 by ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 280:1262-1265. - PubMed
-
- Feige, U., R. Morimoto, I. Yahara, and B. Polla. 1996. Stress-inducible cellular responses. Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, Switzerland.
-
- Gabai, V. L., A. B. Meriin, J. A. Yaglom, J. Y. Wei, D. D. Mosser, and M. Y. Sherman. 2000. Suppression of stress kinase JNK is involved in HSP72-mediated protection of myogenic cells from transient energy deprivation. HSP72 alleviates the stress-induced inhibition of JNK dephosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 275:38088-38094. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
