Activin induces x-zone apoptosis that inhibits luteinizing hormone-dependent adrenocortical tumor formation in inhibin-deficient mice
- PMID: 12748296
- PMCID: PMC155220
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.11.3951-3964.2003
Activin induces x-zone apoptosis that inhibits luteinizing hormone-dependent adrenocortical tumor formation in inhibin-deficient mice
Abstract
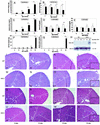
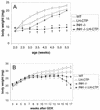
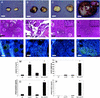
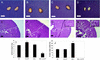
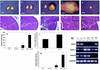
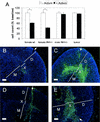
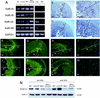
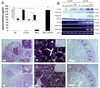
Inhibin and activin are members of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) family of ligands produced and secreted primarily by the gonads and adrenals. Inhibin-null (INH(-/-)) mice develop gonadal tumors and-when gonadectomized-adrenocortical carcinoma. The mechanisms leading to adrenal tumorigenesis have been proposed to involve the lack of a gonadal factor and/or a compensatory increase in gonadotropins. In order to achieve elevation of gonadotropins without the concomitant loss of a gonadal hormone, we crossed INH(-/-) mice with a transgenic mouse strain that has chronically elevated luteinizing hormone (LH) levels (LH-CTP). Compound INH(-/-)-LH-CTP mice die within 6 weeks of age from severe cancer cachexia induced by large, activin-secreting ovarian tumors. Unexpectedly, INH(-/-)-LH-CTP mice not only fail to develop adrenal tumors but have smaller adrenals, with a regressed x zone, indicating that elevated LH levels are not sufficient to induce adrenal tumor formation. However, following gonadectomy, INH(-/-)-LH-CTP mice develop large, sex steroid-producing adrenal tumors that arise from the x zone, indicating a growth-promoting effect of high levels of LH on the adrenal cortex in the absence of ovarian tumors. In addition, in vivo and in vitro data indicate that activin induces apoptosis specifically in the adrenal x zone. The restricted expression of activin receptor subunits and Smad2 in cells of the adrenal x zone, together with the elevated activin levels in INH(-/-)-LH-CTP mice, supports the conclusion that activin inhibits adrenal tumor growth by inducing x-zone regression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High levels of luteinizing hormone analog stimulate gonadal and adrenal tumorigenesis in mice transgenic for the mouse inhibin-alpha-subunit promoter/Simian virus 40 T-antigen fusion gene.Oncogene. 2003 May 22;22(21):3269-78. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206518. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12761497
-
Luteinizing Hormone and GATA4 Action in the Adrenocortical Tumorigenesis of Gonadectomized Female Mice.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(3):1064-1076. doi: 10.1159/000481718. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28977799
-
Expression of activin/inhibin signaling components in the human adrenal gland and the effects of activins and inhibins on adrenocortical steroidogenesis and apoptosis.J Endocrinol. 2003 Sep;178(3):479-89. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1780479. J Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12967339
-
Adrenocortical tumorigenesis in transgenic mice: the role of luteinizing hormone receptor and transcription factors GATA-4 and GATA-61.Reprod Biol. 2001 Jul;1(1):5-9. Reprod Biol. 2001. PMID: 14666170 Review.
-
Inhibins and activins: their roles in the adrenal gland and the development of adrenocortical tumors.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Aug 15;359(1-2):92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.06.005. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 21722704 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibin-A antagonizes TGFbeta2 signaling by down-regulating cell surface expression of the TGFbeta coreceptor betaglycan.Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Mar;24(3):608-20. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0374. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Mol Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20160125 Free PMC article.
-
Review paper: origin and molecular pathology of adrenocortical neoplasms.Vet Pathol. 2009 Mar;46(2):194-210. doi: 10.1354/vp.46-2-194. Vet Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19261630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conditional mutagenesis of Gata6 in SF1-positive cells causes gonadal-like differentiation in the adrenal cortex of mice.Endocrinology. 2013 May;154(5):1754-67. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1892. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23471215 Free PMC article.
-
Current insight into the transient X-zone in the adrenal gland cortex.Vitam Horm. 2024;124:297-339. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2023.05.003. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Vitam Horm. 2024. PMID: 38408801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adrenocortical zonation results from lineage conversion of differentiated zona glomerulosa cells.Dev Cell. 2013 Sep 30;26(6):666-673. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.07.016. Epub 2013 Sep 12. Dev Cell. 2013. PMID: 24035414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beuschlein, F., C. Mutch, D. L. Bavers, Y. M. Ulrich-Lai, W. C. Engeland, C. Keegan, and G. D. Hammer. 2002. Steroidogenic factor-1 is essential for compensatory adrenal growth following unilateral adrenalectomy. Endocrinology 143:3122-3135. - PubMed
-
- Billiar, R. B., M. G. Leavitt, P. Smith, E. D. Albrecht, and G. J. Pepe. 1999. Functional capacity of fetal zone cells of the baboon fetal adrenal gland: a major source of α-inhibin. Biol. Reprod. 61:142-146. - PubMed
-
- Chen, Y. G., H. M. Lui, S. L. Lin, J. M. Lee, and S. Y. Ying. 2002. Regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis by activin. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 227:75-87. - PubMed
-
- Cipriano, S. C., L. Chen, K. H. Burns, A. Koff, and M. M. Matzuk. 2001. Inhibin and p27 interact to regulate gonadal tumorigenesis. Mol. Endocrinol. 15:985-996. - PubMed
-
- Coerver, K. A., T. K. Woodruff, M. J. Finegold, J. Mather, A. Bradley, and M. M. Matzuk. 1996. Activin signaling through activin receptor type II causes the cachexia-like symptoms in inhibin-deficient mice. Mol. Endocrinol. 10:534-543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
