CD137 costimulatory T cell receptor engagement reverses acute disease in lupus-prone NZB x NZW F1 mice
- PMID: 12750400
- PMCID: PMC155050
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI17662
CD137 costimulatory T cell receptor engagement reverses acute disease in lupus-prone NZB x NZW F1 mice
Abstract
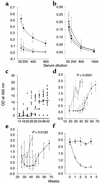
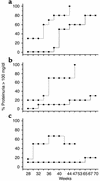
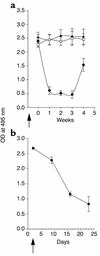
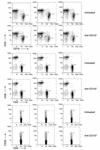
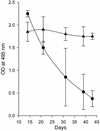
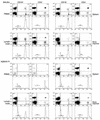
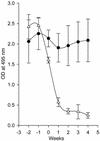
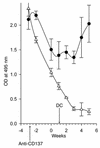
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a CD4(+) T cell-dependent, immune complex-mediated, autoimmune disease that primarily affects women of childbearing age. Generation of high-titer affinity-matured IgG autoantibodies, specific for double-stranded DNA and other nuclear antigens, coincides with disease progression. Current forms of treatment of SLE including glucocorticosteroids are often inadequate and induce severe side effects. Immunological approaches for treating SLE in mice using anti-CD4 mAb's or CTLA4-Ig and anti-CD154 mAb's have proven to be effective. However, like steroid treatment, these regimens induce global immunosuppression, and their withdrawal allows for disease progression. In this report we show that lupus-prone NZB x NZW F(1) mice given three injections of anti-CD137 (4-1BB) mAb's between 26 and 35 weeks of age reversed acute disease, blocked chronic disease, and extended the mice's lifespan from 10 months to more than 2 years. Autoantibody production in recipients was rapidly suppressed without inducing immunosuppression. Successful treatment could be traced to the fact that NZB x NZW F(1) mice, regardless of their age or disease status, could not maintain pathogenic IgG autoantibody production in the absence of continuous CD4(+) T cell help. Our data support the hypothesis that CD137-mediated signaling anergized CD4(+) T cells during priming at the DC interface.
Figures
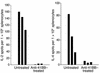
References
-
- Wakeland EK, Liu K, Graham RR, Behrens TW. Delineating the genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity. 2001;15:397–408. - PubMed
-
- Stott DI, Merino J, Schurmans S, Lambert PH. Expression of anti-DNA clonotypes and the role of helper T-lymphocytes during the autoimmune response in mice tolerant to alloantigens. Autoimmunity. 1988;1:253–266. - PubMed
-
- Humbert M, Galanaud P. B-lymphocyte hyperreactivity and differentiation factors of T-lymphocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Med. Interne (Paris). 1990;141:213–216. - PubMed
-
- Sobel ES, et al. T-B collaboration for autoantibody production in lpr mice is cognate and MHC-restricted. J. Immunol. 1994;152:6011–6016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

