Pacemaker channel dysfunction in a patient with sinus node disease
- PMID: 12750403
- PMCID: PMC155041
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI16387
Pacemaker channel dysfunction in a patient with sinus node disease
Abstract
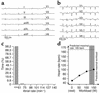
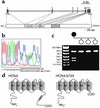
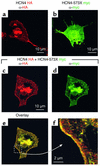
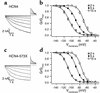
The cardiac pacemaker current I(f) is a major determinant of diastolic depolarization in sinus nodal cells and has a key role in heartbeat generation. Therefore, we hypothesized that some forms of "idiopathic" sinus node dysfunction (SND) are related to inherited dysfunctions of cardiac pacemaker ion channels. In a candidate gene approach, a heterozygous 1-bp deletion (1631delC) in exon 5 of the human HCN4 gene was detected in a patient with idiopathic SND. The mutant HCN4 protein (HCN4-573X) had a truncated C-terminus and lacked the cyclic nucleotide-binding domain. COS-7 cells transiently transfected with HCN4-573X cDNA indicated normal intracellular trafficking and membrane integration of HCN4-573X subunits. Patch-clamp experiments showed that HCN4-573X channels mediated I(f)-like currents that were insensitive to increased cellular cAMP levels. Coexpression experiments showed a dominant-negative effect of HCN4-573X subunits on wild-type subunits. These data indicate that the cardiac I(f) channels are functionally expressed but with altered biophysical properties. Taken together, the clinical, genetic, and in vitro data provide a likely explanation for the patient's sinus bradycardia and the chronotropic incompetence.
Figures

References
-
- Lamas GA, et al. The mode selection trial (MOST) in sinus node dysfunction: design, rationale, and baseline characteristics of the first 1000 patients. Am. Heart J. 2000;140:541–551. - PubMed
-
- Sarachek NS, Leonard JL. Familial heart block and sinus bradycardia. Classification and natural history. Am. J. Cardiol. 1972;29:451–458. - PubMed
-
- Spellberg RD. Familial sinus node disease. Chest. 1971;60:246–251. - PubMed
-
- Mackintosh AF, Chamberlain DA. Sinus node disease affecting both parents and both children. Eur. J. Cardiol. 1979;10:117–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

