Aquaporin-1 and HCO3(-)-Cl- transporter-mediated transport of CO2 across the human erythrocyte membrane
- PMID: 12754312
- PMCID: PMC2343058
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.040113
Aquaporin-1 and HCO3(-)-Cl- transporter-mediated transport of CO2 across the human erythrocyte membrane
Abstract
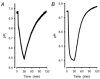
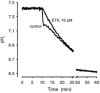
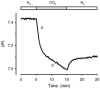
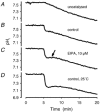
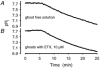
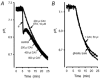
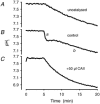
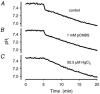
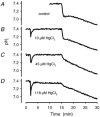
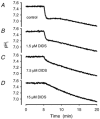
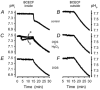
Recent studies have suggested that aquaporin-1 (AQP1) as well as the HCO3(-)-Cl- transporter may be involved in CO2 transport across biological membranes, but the physiological importance of this route of gas transport remained unknown. We studied CO2 transport in human red blood cell ghosts at physiological temperatures (37 degrees C). Replacement of inert with CO2-containing gas above a stirred cell suspension caused an outside-to-inside directed CO2 gradient and generated a rapid biphasic intracellular acidification. The gradient of the acidifying gas was kept small to favour high affinity entry of CO2 passing the membrane. All rates of acidification except that of the approach to physicochemical equilibrium of the uncatalysed reaction were restricted to the intracellular environment. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase (CA) demonstrated that CO2-induced acidification required the catalytic activity of CA. Blockade of the function of either AQP1 (by HgCl2 at 65 microM) or the HCO3(-)-Cl- transporter (by DIDS at 15 microM) completely prevented fast acidification. These data indicate that, at low chemical gradients for CO2, nearly the entire CO2 transport across the red cell membrane is mediated by AQP1 and the HCO3--Cl- transporter. Therefore, these proteins may function as high affinity sites for CO2 transport across the erythrocyte membrane.
Figures
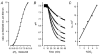
References
-
- Cooper GJ, Boron WF. Effect of pCMBS on CO2 permeability of Xenopus oocytes expressing aquaporin 1 or its C189S mutant. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:C1481–1486. - PubMed
-
- Denker BM, Smith BL, Kuhajda FP, Agre P. Identification, purification, and partial characterization of a novel Mr 28,000 integral membrane protein from erythrocytes and renal tubules. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:15634–15642. - PubMed
-
- Dodge JT, Mitchell C, Hanahan DJ. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963;100:119–130. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

