The basic helix-loop-helix-PAS protein ARNT functions as a potent coactivator of estrogen receptor-dependent transcription
- PMID: 12754377
- PMCID: PMC164478
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1136688100
The basic helix-loop-helix-PAS protein ARNT functions as a potent coactivator of estrogen receptor-dependent transcription
Abstract
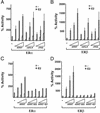
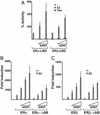
The biological effects of estrogens are mediated by the estrogen receptors ERalpha and ERbeta. These receptors regulate gene expression through binding to DNA enhancer elements and subsequently recruiting factors such as coactivators that modulate their transcriptional activity. Here we show that ARNT (aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator), the obligatory heterodimerization partner for the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha, functions as a potent coactivator of ERalpha- and ERbeta- dependent transcription. The coactivating effect of ARNT depends on physical interaction with the ERs and involves the C-terminal domain of ARNT and not the structurally conserved basic helix-loop-helix and PAS (Per-ARNT-Sim) motifs. Moreover, we show that ARNT/ER interaction requires the E2-activated ligand binding domain of ERalpha or ERbeta. These observations, together with the previous role of ARNT as an obligatory partner protein for conditionally regulated basic helix-loop-helix-PAS proteins like the aryl hydrocarbon receptor or hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha, expand the cellular functions of ARNT to include regulation of ERalpha and ERbeta transcriptional activity. ARNT was furthermore recruited to a natural ER target gene promoter in a estrogen-dependent manner, supporting a physiological role for ARNT as an ER coactivator.
Figures

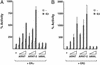

References
-
- Nilsson, S., Makela, S., Treuter, E., Tujague, M., Thomsen, J., Andersson, G., Enmark, E., Pettersson, K., Warner, M. & Gustafsson, J. A. (2001) Physiol. Rev. 81, 1535–1565. - PubMed
-
- Pettersson, K. & Gustafsson, J. (2001) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 63, 165–192. - PubMed
-
- Aranda, A. & Pascual, A. (2001) Physiol. Rev. 81, 1269–1304. - PubMed
-
- Urnov, F. D. & Wolffe, A. P. (2001) Oncogene 20, 2991–3006. - PubMed
-
- Narlikar, G. J., Fan, H. Y. & Kingston, R. E. (2002) Cell 108, 475–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

