Steroid hormone synthesis by vaccinia virus suppresses the inflammatory response to infection
- PMID: 12756265
- PMCID: PMC2193778
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20022201
Steroid hormone synthesis by vaccinia virus suppresses the inflammatory response to infection
Abstract
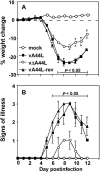
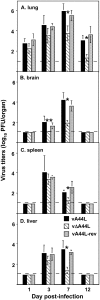
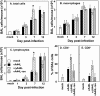
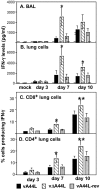
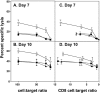
The 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3beta-HSD) isoenzymes play a key role in cellular steroid hormone synthesis. Vaccinia virus (VV) also synthesizes steroid hormones with a 3beta-HSD enzyme (v3beta-HSD) encoded by gene A44L. Here we examined the effects of v3beta-HSD in VV disease using wild-type (vA44L), deletion (vDeltaA44L), and revertant (vA44L-rev) viruses in a murine intranasal model. Loss of A44L was associated with an attenuated phenotype. Early (days 1-3) after infection with vDeltaA44L or control viruses the only difference observed between groups was the reduced corticosterone level in lungs and plasma of vDeltaA44L-infected animals. Other parameters examined (body weight, signs of illness, temperature, virus titres, the pulmonary inflammatory infiltrate, and interferon [IFN]-gamma levels) were indistinguishable between groups. Subsequently, vDeltaA44L-infected animals had reduced weight loss and signs of illness, and displayed a vigorous pulmonary inflammatory response. This was characterized by rapid recruitment of CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes, enhanced IFN-gamma production and augmented cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity. These data suggest that steroid production by v3beta-HSD contributes to virus virulence by inhibiting an effective inflammatory response to infection.
Figures


References
-
- Labrie, F., J. Simard, V. Luu-The, G. Pelletier, A. Belanger, Y. Lachance, H.F. Zhao, C. Labrie, N. Breton, Y. de Launoit, et al. 1992. Structure and tissue-specific expression of 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/5-ene-4-ene isomerase genes in human and rat classical and peripheral steroidogenic tissues. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 41:421–435. - PubMed
-
- Pelletier, G., E. Dupont, J. Simard, V. Luu-The, A. Belanger, and F. Labrie. 1992. Ontogeny and subcellular localization of 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3 beta-HSD) in the human and rat adrenal, ovary and testis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 43:451–467. - PubMed
-
- Martel, C., M.H. Melner, D. Gagne, J. Simard, and F. Labrie. 1994. Widespread tissue distribution of steroid sulfatase, 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta 5-delta 4 isomerase (3 beta-HSD), 17 beta-HSD 5 alpha-reductase and aromatase activities in the rhesus monkey. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 104:103–111. - PubMed
-
- Morel, Y., F. Mebarki, E. Rheaume, R. Sanchez, M.G. Forest, and J. Simard. 1997. Structure-function relationships of 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: contribution made by the molecular genetics of 3 beta- hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency. Steroids. 62:176–184. - PubMed
-
- Boumpas, D.T., G.P. Chrousos, R.L. Wilder, T.R. Cupps, and J.E. Balow. 1993. Glucocorticoid therapy for immune-mediated diseases: basic and clinical correlates. Ann. Intern. Med. 119:1198–1208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

