NIM-R7, a novel marker for resting B1 and marginal-zone B lymphocytes, is also expressed on activated T and B cells
- PMID: 12757618
- PMCID: PMC1782968
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01647.x
NIM-R7, a novel marker for resting B1 and marginal-zone B lymphocytes, is also expressed on activated T and B cells
Abstract
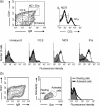
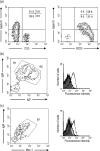
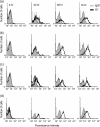
In mice, follicular B cells have been studied in detail, while two other B-cell subpopulations - marginal-zone B and B1 cells - are less well understood. In this work we report the expression pattern of p58, a lymphocyte-activation marker, recognized by rat monoclonal antibody, NIM-R7, and present on the latter two cell subpopulations. Staining with NIM-R7 showed that undisturbed marginal-zone B cells, as well as peritoneal cavity and splenic B1a cells, constitutively expressed p58, whereas follicular B cells and resting T lymphocytes did not. Ontogenic analysis of different compartments showed that p58 did not appear at any stage of development, prior to the development of mature T or B2 lymphocytes. Upon polyclonal stimulation, however, p58 appeared on both T and B2 lymphocytes. Finally, ricin A-conjugated NIM-R7 was able to kill the BCL1 lymphoma without effect on mature resting B2 cells. Therefore, p58 may be a potential target for diagnosis or therapy of B1 and marginal-zone B-cell malignancies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IgMhighCD21high lymphocytes enriched in the splenic marginal zone generate effector cells more rapidly than the bulk of follicular B cells.J Immunol. 1999 Jun 15;162(12):7198-207. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10358166
-
Fc receptor homolog 3 is a novel immunoregulatory marker of marginal zone and B1 B cells.J Immunol. 2006 Nov 15;177(10):6815-23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.10.6815. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17082595
-
CD1 expression defines subsets of follicular and marginal zone B cells in the spleen: beta 2-microglobulin-dependent and independent forms.J Immunol. 1998 Aug 15;161(4):1710-7. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9712035
-
CD44-stimulated dendrite formation ('spreading') in activated B cells.Immunology. 1997 Jan;90(1):147-53. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1997.00126.x. Immunology. 1997. PMID: 9038725 Free PMC article.
-
Development and selection of marginal zone B cells.Immunol Rev. 2004 Feb;197:192-205. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.0112.x. Immunol Rev. 2004. PMID: 14962196 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunotoxins constructed with ribosome-inactivating proteins and their enhancers: a lethal cocktail with tumor specific efficacy.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(42):6584-643. doi: 10.2174/1381612820666140826153913. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 25341935 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hardy RR. Murine B cell differentiation in fetal liver and adult bone marrow. In: Herzenberg L, Weir DM, Herzenberg L, Blackwell C, editors. Weir's Handbook of Experimental Immunology. 5. Oxford: Blackwell Science Inc.; 1996. pp. 82.1–82.8.
-
- Rothstein TL. Cutting edge commentary: two B-1 or not to be one. J Immunol. 2002;168:4257–61. - PubMed
-
- Tarlinton D. Germinal centers: form and function. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998;10:245–51. - PubMed
-
- Martin F, Oliver AM, Kearney JF. Marginal zone and B1 B cells unite in the early response against T-independent blood-borne particulate antigens. Immunity. 2001;14:617–29. - PubMed
-
- Herzenberg LA. B-1 cells: the lineage question revisited. Immunol Rev. 2000;175:9–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

