Effect of cytofectins on the immune response of murine macrophages to mammalian DNA
- PMID: 12757621
- PMCID: PMC1782966
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01653.x
Effect of cytofectins on the immune response of murine macrophages to mammalian DNA
Abstract
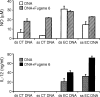
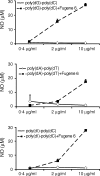
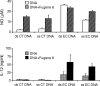
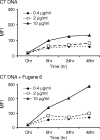
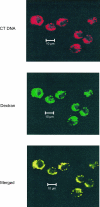
DNA, depending on base sequence, can induce a wide range of immune responses. While bacterial DNA is stimulatory, mammalian DNA is inactive alone and can, moreover, inhibit the response to bacterial DNA. To determine whether the mode of cell entry affects the immune properties of mammalian DNA, we have investigated the effects of the cytofectin agents Fugene 6 (Roche Diagnostics Corp., Indianapolis, IN), Lipofectin and Lipofectamine (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY) on the responses of murine macrophages to DNA from calf thymus and human placenta. Whereas calf thymus and human placenta DNA alone failed to stimulate J774 or RAW264.7 cell lines or bone marrow-derived macrophages, these DNAs in complexes with cytofectin agents stimulated macrophages to produce nitric oxide but not interleukin 12. Both single-stranded and double-stranded DNAs were active in the presence of cytofectins. Macrophage activation by the DNA-cytofectin complexes was reduced by chloroquine, suggesting a role of endosomal acidification in activation. As shown by flow cytometry and confocal microscopy, the cytofectins caused an increase in the uptake of DNA into cells. Our findings indicate that macrophages vary in their response to DNA depending on uptake pathway, suggesting that activation by DNA reflects not only sequence but also context or intracellular location.
Figures
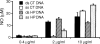
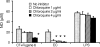
References
-
- Tokunaga T, Yamamoto H, Shimada S, et al. Antitumor activity of deoxyribonucleic acid fraction from Mycobacterium bovis BCG. I. Isolation, physicochemical characterization, and antitumor activity. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984;72:955–62. - PubMed
-
- Messina JP, Gilkeson GS, Pisetsky DS. Stimulation of in vitro murine lymphocyte proliferation by bacterial DNA. J Immunol. 1991;147:1759–64. - PubMed
-
- Krieg AM, Yi AK, Matson S, Waldschmidt TJ, Bishop GA, Teasdale R, Koretzky GA, Klinman DM. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA trigger direct B-cell activation. Nature. 1995;374:546–9. - PubMed
-
- Pisetsky DS, Reich CF. Inhibition of murine macrophage IL-12 production by natural and synthetic DNA. Clin Immunol. 2000;96:198–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

