Differential expression of the angiogenic factor genes vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and endocrine gland-derived VEGF in normal and polycystic human ovaries
- PMID: 12759245
- PMCID: PMC1868136
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64322-2
Differential expression of the angiogenic factor genes vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and endocrine gland-derived VEGF in normal and polycystic human ovaries
Abstract
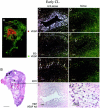
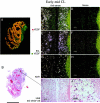
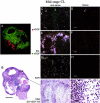
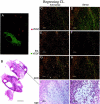
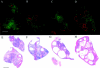
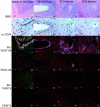
Angiogenesis is a key aspect of the dynamic changes occurring during the normal ovarian cycle. Hyperplasia and hypervascularity of the ovarian theca interna and stroma are also prominent features of the polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a leading cause of infertility. Compelling evidence indicated that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a key mediator of the cyclical corpus luteum angiogenesis. However, the nature of the factor(s) that mediate angiogenesis in PCOS is less clearly understood. Endocrine gland-derived (EG)-VEGF has been recently identified as an endothelial cell mitogen with selectivity for the endothelium of steroidogenic glands and is expressed in normal human ovaries. In the present study, we compared the expression of EG-VEGF and VEGF mRNA in a series of 13 human PCOS and 13 normal ovary specimens by in situ hybridization. EG-VEGF expression in normal ovaries is dynamic and generally complementary to VEGF expression in both follicles and corpora lutea. A particularly high expression of EG-VEGF was detected in the Leydig-like hilus cells found in the highly vascularized ovarian hilus. In PCOS ovaries, we found strong expression of EG-VEGF mRNA in theca interna and stroma in most of the specimens examined, thus spatially related to the new blood vessels. In contrast, VEGF mRNA expression was most consistently associated with the granulosa cell layer and sometimes the theca, but rarely with the stroma. These findings indicate that both EG-VEGF and VEGF are expressed in PCOS ovaries, but in different cell types at different stages of differentiation, thus suggesting complementary functions for the two factors in angiogenesis and possibly cyst formation.
Figures



References
-
- Bassett DL: The changes in the vascular pattern of the ovary of the albino rat during the estrous cycle. Am J Anat 1943, 73:251-278
-
- Zeleznik AJ, Schuler HM, Reichert LE, Jr: Gonadotropin-binding sites in the rhesus monkey ovary: role of the vasculature in the selective distribution of human chorionic gonadotropin to the preovulatory follicle. Endocrinology 1981, 109:356-362 - PubMed
-
- Carr BR, MacDonald PC, Simpson ER: The role of lipoproteins in the regulation of progesterone secretion by the corpus luteum. Fertil Steril 1981, 38:303-311 - PubMed
-
- Goede V, Schmidt T, Kimmina S, Kozian D, Augustin HG: Analysis of blood vessel maturation processes during cyclic ovarian angiogenesis. Lab Invest 1998, 78:1385-1394 - PubMed
-
- Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, Bartunkova S, Wiegend SJ, Radziejewski C, Compton D, McClain J, Aldrich TH, Papadopulos N, Daly TJ, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD: Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie-2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science 1997, 277:55-60 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

