Angiogenic actions of angiopoietin-1 require endothelium-derived nitric oxide
- PMID: 12759249
- PMCID: PMC1868142
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64326-X
Angiogenic actions of angiopoietin-1 require endothelium-derived nitric oxide
Abstract
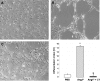
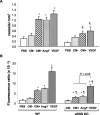
Angiopoietin1 (Ang1) is a novel angiogenic factor with important actions on endothelial cell (EC) differentiation and vascular maturation. Ang1 has been shown to prevent EC apoptosis through activation of PI3-kinase/Akt, a pathway that is also known to activate endothelium nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). Therefore, we hypothesized that the angiogenic effects of Ang1 would also be dependent on the PI3-kinase/Akt pathway, possibly mediated by increased eNOS activity and NO release. Treatment of human umbilical vein endothelial cells with recombinant Ang1* (300 ng/ml) for 15 minutes resulted in PI3-kinase-dependent Akt phosphorylation, comparable to that observed with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) (50 ng/ml), and increased NO production in a PI3-kinase/Akt-dependent manner. Capillary-like tube formation induced by Ang1* in fibrin matrix at 24 hours (differentiation index, DI: 13.74 +/- 0.76 versus control 1.71 +/- 0.31) was abolished in the presence of the selective PI3-kinase inhibitor, LY294002 (50 micro mol/L) (DI: 0.31 +/- 0.31, P < 0.01) or the NOS inhibitor, L-NAME (3 mmol/L) (DI: 4.10 +/- 0.59, P < 0.01). In subcutaneous Matrigel implants in vivo, addition of recombinant Ang1* or wild-type Ang1 from conditioned media of COS-1 cells transfected with a pFLAG Ang1 expression vector, induced significant neovascularization to a degree similar to VEGF. Finally, angiogenesis in vivo in response to both Ang1 and VEGF was significantly reduced in eNOS-deficient compared with wild-type mice. In summary, our results demonstrate for the first time that endothelial-derived NO is required for Ang1-induced angiogenesis, and that the PI3-kinase signaling mediates the activation of eNOS and NO release in response to Ang1.
Figures





References
-
- Davis S, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, Acheson A, Compton DL, Jain V, Ryan TE, Bruno J, Radziejewski C, Maisonpierre PC, Yancopoulos GD: Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell 1996, 87:1161-1169 - PubMed
-
- Dumont DJ, Gradwohl G, Fong GH, Puri MC, Gertsenstein M, Auerbach A, Breitman ML: Dominant-negative and targeted null mutations in the endothelial receptor tyrosine kinase, tek, reveal a critical role in vasculogenesis of the embryo. Genes Dev 1994, 8:1897-1909 - PubMed
-
- Sato TN, Tozawa Y, Deutsch U, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Fujiwara Y, Gendron-Maguire M, Gridley T, Wolburg H, Risau W, Qin Y: Distinct roles of the receptor tyrosine kinases Tie-1 and Tie-2 in blood vessel formation. Nature 1995, 376:70-74 - PubMed
-
- Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, Bartunkova S, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD: Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 1996, 87:1171-1180 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

