Comparison of assays for the detection of West Nile virus antibodies in chicken serum
- PMID: 12760478
- PMCID: PMC227040
Comparison of assays for the detection of West Nile virus antibodies in chicken serum
Abstract
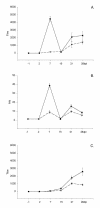
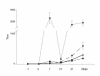
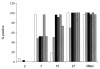
Six tests for the detection of West Nile virus (WNV) antibodies in the serum of experimentally infected chickens were compared. The tests included the hemagglutination-inhibition test (HIT), immunoglobulin M (IgM)-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with WNV-infected mouse brain antigen, immunoglobulin G (IgG) indirect ELISA with tickborne encephalitis viral antigen, the microtitre virus neutralization test, the standard plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT), and the microtitre PRNT (micro-PRNT). Thirty adult chickens, intravenously and intramuscularly inoculated with 10(7) plaque-forming units (PFU) of WNV strain Egypt 101, were bled and given a booster of 10(7) PFU at 7,15, and 21 d postinoculation; the final blood collection was on day 28. Although the micro-PRNT is capable of detecting the highest antibody titres during both early and late infection, because of the technical complexity and time requirements of this test a combination of IgM and IgG ELISAs is recommended for serologic screening. Serum samples that give positive results in the ELISAs can then be tested by the micro-PRNT to determine the specificity of antibodies to WNV.
Figures
References
-
- Outbreak of West Nile-like viral encephalitis — New York, 1999. Morbid Mortal Wkly Rep 1999;48:845–849. - PubMed
-
- Weekly Update: West Nile virus activity — United States, November 14–20, 2001. Morbid Mortal Wkly Rep 2001;50:1061–1062. - PubMed
-
- Cernescu C, Nedelcu NI, Tardei G, Ruta S, Tsai TF. Continued transmission of West Nile virus to humans in Southeastern Romania, 1997–1998. J Infect Dis 2000;181:710–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
