Generation of stable cell lines expressing Lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus for antiviral-compound screening
- PMID: 12760870
- PMCID: PMC155849
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.6.1936-1942.2003
Generation of stable cell lines expressing Lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus for antiviral-compound screening
Abstract
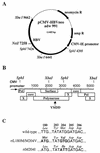
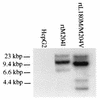
Lamivudine [beta-L-(-)-2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine] is a potent inhibitor of hepadnavirus replication and is used both to treat chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections and to prevent reinfection of transplanted livers. Unfortunately, lamivudine-resistant HBV variants do arise during prolonged therapy, indicating a need for additional antiviral drugs. Replication-competent HBV constructs containing the reverse transcriptase domain L180M/M204V and M204I (rtL180M/M204V and rtM204I) mutations associated with lamivudine resistance were used to produce stable cell lines that express the resistant virus. These cell lines contain stable integrations of HBV sequences and produce both intracellular and extracellular virus. HBV produced by these cell lines was shown to have a marked decrease in sensitivity to lamivudine, with 450- and 3,000-fold shifts in the 50% inhibitory concentrations for the rtM204I and rtL180M/M204V viruses, respectively, compared to that for the wild-type virus. Drug assays indicated that the lamivudine-resistant virus exhibited reduced sensitivity to penciclovir [9-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethyl-but-1-yl) guanine] but was still inhibited by the nucleoside analogues CDG (carbocyclic 2'-deoxyguanosine) and abacavir ([1S,4R]-4-[2-amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-1-methanol). Screening for antiviral compounds active against the lamivudine-resistant HBV can now be done with relative ease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of novel human hepatoma cell lines with stable hepatitis B virus secretion for evaluating new compounds against lamivudine- and penciclovir-resistant virus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000 Dec;44(12):3402-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.44.12.3402-3407.2000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000. PMID: 11083647 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro susceptibility of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus to adefovir and tenofovir.Antivir Ther. 2004 Jun;9(3):353-63. Antivir Ther. 2004. PMID: 15259898
-
Investigation into drug-resistant mutations of HBV from 845 nucleoside/nucleotide analogue-naive Chinese patients with chronic HBV infection.Antivir Ther. 2015;20(2):141-7. doi: 10.3851/IMP2813. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Antivir Ther. 2015. PMID: 24992206
-
Hepatitis B virus resistance to lamivudine and its clinical implications.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2002 May;13(3):143-55. doi: 10.1177/095632020201300301. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2002. PMID: 12448687 Review.
-
Resistance of hepatitis B virus to antiviral drugs: current aspects and directions for future investigation.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2001 Jan;12(1):1-35. doi: 10.1177/095632020101200101. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11437320 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel fluoronucleoside analog NCC inhibits lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus in a hepatocyte model.Braz J Infect Dis. 2018 Nov-Dec;22(6):477-486. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2018.11.005. Epub 2018 Dec 23. Braz J Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30586543 Free PMC article.
-
Virologic monitoring of hepatitis B virus therapy in clinical trials and practice: recommendations for a standardized approach.Gastroenterology. 2008 Feb;134(2):405-15. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.11.036. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18242209 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allen, M., M. Deslauriers, C. Andrews, G. Tipples, K. Walters, D. Tyrrell, N. Brown, L. Condreay et al. 1998. Identification and characterization of mutations in hepatitis B virus resistant to lamivudine. Hepatology 27:1670-1677. - PubMed
-
- Bain, V., N. Kneteman, M. Ma, K. Gutfreund, J. Shapiro, K. Fischer, G. Tipples, H. Lee, L. Jewell, and D. Tyrrell. 1996. Efficacy of lamivudine in chronic hepatitis B patients with active viral replication and decompensated cirrhosis undergoing liver transplantation. Transplantation 62:1456-1462. - PubMed
-
- Beasley, R. 1988. Hepatitis B virus. The major etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 61:1942-1956. - PubMed
-
- Beasley, R., L. Hwang, C. Lin, and C. Chien. 1981. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22,707 men in Taiwan. Lancet ii:1129-1133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

