Stability and antibacterial activity of cefepime during continuous infusion
- PMID: 12760882
- PMCID: PMC155835
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.6.1991-1994.2003
Stability and antibacterial activity of cefepime during continuous infusion
Abstract
The stability of cefepime during simulated continuous infusion was determined with a motorized portable infusion pump worn over a period of 24 to 36 h. Susceptibility testing on cefepime solutions over time indicates that the degradation products do not exhibit antibacterial activity. Cefepime stability at 24 h following continuous infusion was 94.3% +/- 1.0%, which supports the use of continuous infusion.
Figures

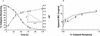
References
-
- Arguedas, A. G., H. R. Stutman, M. Zaleska, C. A. Knupp, M. I. Marks, and E. Nussbaum. 1992. Cefepime pharmacokinetics and clinical response in patients with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Dis. Child. 146:797-802. - PubMed
-
- Craig, W. A. 2002. Pharmacodynamics of antimicrobials: general concepts and applications, p. 1-22. In C. H. Nightingale (ed.), Antimicrobial pharmacodynamics in theory and clinical practice. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, N.Y.
-
- Elkhaili, H., L. Linger, H. Monteil, and F. Jehl. 1997. High-performance liquid chromatographic assay for cefepime in serum. J. Chromatogr. B 690:181-188. - PubMed
-
- Fubara, J. O., and R. E. Notari. 1998. Influence of pH, temperature and buffers on cefepime degradation kinetics and stability predictions in aqueous solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 87:1572-1576. - PubMed
-
- Fubara, J. O., and R. E. Notari. 1997. A kinetic oxymoron: concentration-dependent first-order rate constants for hydrolysis of ceftazidime. J. Pharm. Sci. 87:53-57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

