Antigenic organization of the N-terminal part of the polymorphic outer membrane proteins 90, 91A, and 91B of Chlamydophila abortus
- PMID: 12761105
- PMCID: PMC155774
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.6.3240-3250.2003
Antigenic organization of the N-terminal part of the polymorphic outer membrane proteins 90, 91A, and 91B of Chlamydophila abortus
Abstract
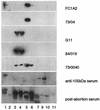
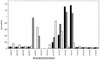
A series of overlapping recombinant antigens, 61 to 74 residues in length, representing polymorphic outer membrane protein 90 (POMP90) of Chlamydophila abortus and two recombinant peptides spanning gene fragment p91Bf99 of POMP91B were assessed by immunoblotting to determine the antigen-binding sites of 20 monoclonal antibodies to POMP90, -91A, and -91B. The epitopes were further restricted by scanning 52 overlapping synthetic 12-mer peptides representing the N-terminal part of POMP90, and the 12-mer epitopes were then analyzed by using hexapeptides to the resolution of a single amino acid. Ten epitopes were defined: 1, TSEEFQVKETSSGT; 2, SGAIYTCEGNVCISYAGKDSPL; 3, SLVFHKNCSTAE; 4, AIYADKLTIVSGGPTLFS; 5, SPKGGAISIKDS; 6, ITFDGNKIIKTS; 7, LRAKDGFGIFFY; 7a, DGFGIF; 7b, GIFFYD; 8, IFFYDPITGGGS; 8a, FFYDPIT; 9, GKIVFSGE; and 10, DLGTTL. The 20-mer peptide LRAKDGFGIFFYDPITGGGS was a major epitope that was recognized by seven antibodies. Epitopes 7 to 10 were conserved in reference strains of the former species C. psittaci, whereas the strong antigenic peptides FYDPIT and IVFSGE were conserved among members of the genus CHLAMYDOPHILA: Epitopes 3 to 8 were located within the best-scoring beta-helical wrap (residues 148 to 293) predicted for POMP91B by the program BETAWRAP. Other studies have suggested an association of the POMPs with type V secretory autotransporter proteins. The results presented in this study provide some evidence for a passenger domain that is folded as a beta-helix pyramid with compact antigenic organization.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Serological diagnosis of ovine enzootic abortion by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a recombinant protein fragment of the polymorphic outer membrane protein POMP90 of Chlamydophila abortus.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Nov;40(11):4235-43. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.11.4235-4243.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12409404 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphic outer-membrane proteins of Chlamydophila abortus are glycosylated.Microbiology (Reading). 2001 Dec;147(Pt 12):3303-10. doi: 10.1099/00221287-147-12-3303. Microbiology (Reading). 2001. PMID: 11739762
-
Diagnosis of ovine enzootic abortion using an indirect ELISA (rOMP91B iELISA) based on a recombinant protein fragment of the polymorphic outer membrane protein POMP91B of Chlamydophila abortus.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001 Feb 20;195(2):157-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10514.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11179645
-
Identification of protective epitopes by sequencing of the major outer membrane protein gene of a variant strain of Chlamydia psittaci serotype 1 (Chlamydophila abortus).Infect Immun. 2001 Jan;69(1):607-12. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.1.607-612.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11119563 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope analysis of an immunodominant domain on the P1 protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b using synthetic peptides and anti-idiotypic antibodies.Microb Pathog. 1992 Jun;12(6):433-42. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90006-a. Microb Pathog. 1992. PMID: 1522798
Cited by
-
Identification of immunologically relevant proteins of Chlamydophila abortus using sera from experimentally infected pregnant ewes.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010 Aug;17(8):1274-81. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00163-10. Epub 2010 Jun 16. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20554807 Free PMC article.
-
The Chlamydophila abortus genome sequence reveals an array of variable proteins that contribute to interspecies variation.Genome Res. 2005 May;15(5):629-40. doi: 10.1101/gr.3684805. Epub 2005 Apr 18. Genome Res. 2005. PMID: 15837807 Free PMC article.
-
Members of the Pmp protein family of Chlamydia pneumoniae mediate adhesion to human cells via short repetitive peptide motifs.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Nov;78(4):1004-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07386.x. Epub 2010 Oct 6. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21062373 Free PMC article.
-
Immune response to Chlamydophila abortus POMP91B protein in the context of different Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMP); role of antigen in the orientation of immune response.Toxins (Basel). 2009 Dec;1(2):59-73. doi: 10.3390/toxins1020059. Epub 2009 Oct 13. Toxins (Basel). 2009. PMID: 22069532 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization Against Chlamydia trachomatis Polymorphic Membrane Protein D Tetrapeptide Motifs Limits Early Female Reproductive Tract Infection in a Mouse Model.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Feb 25;13(3):234. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13030234. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40266062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buendia, A. J., J. Salinas, J. Sanchez, M. C. Gallego, A. Rodolakis, and F. Cuello. 1997. Localization by immunoelectron microscopy of antigens of Chlamydia psittaci suitable for diagnosis or vaccine development. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 150:113-119. - PubMed
-
- Cevenini, R., A. Moroni, V. Sambri, S. Perini, and M. La Placa. 1989. Serological response to chlamydial infection in sheep, studied by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunoblotting. FEMS Microbiol. Immunol. 47:459-464. - PubMed
-
- Cevenini, R., M. Donati, E. Brocchi, F. de Simone, and M. La Placa. 1991. Partial characterization of an 89-kDa highly immunoreactive protein from Chlamydia psittaci A/22 causing ovine abortion. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 65:111-115. - PubMed
-
- Everett, K. D. E., R. M. Bush, and A. A. Andersen. 1999. Emended description of the order Chlamydiales, proposal of Parachlamydiaceae fam. nov. and Simcaniaceae fam. nov., each containing one monotypic genus, revised taxonomy of the family Chlamydiaceae, including a new genus and five new species, and standards for the identification of organisms. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49:415-440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

