pH-regulated gene expression of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 12761138
- PMCID: PMC155744
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.6.3529-3539.2003
pH-regulated gene expression of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
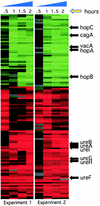
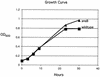
Colonization by the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori has been shown to be intricately linked to the development of gastritis, ulcers, and gastric malignancy. Little is known about mechanisms employed by the bacterium that help it adapt to the hostile environment of the human stomach. In an effort to extend our knowledge of these mechanisms, we utilized spotted-DNA microarrays to characterize the response of H. pylori to low pH. Expression of approximately 7% of the bacterial genome was reproducibly altered by shift to low pH. Analysis of the differentially expressed genes led to the discovery that acid exposure leads to profound changes in motility of H. pylori, as a larger percentage of acid-exposed bacterial cells displayed motility and moved at significantly higher speeds. In contrast to previous publications, we found that expression of the bacterial virulence gene cagA was strongly repressed by acid exposure. Furthermore, this transcriptional repression was reflected at the level of protein accumulation in the H. pylori cell.
Figures

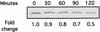

Similar articles
-
Iron and pH homeostasis intersect at the level of Fur regulation in the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori.Infect Immun. 2006 Jan;74(1):602-14. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.1.602-614.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16369017 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of cagA, virB/D Complex and/or vacA Genes in Helicobacter pylori Strains Originating from Patients with Gastric Diseases.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 11;11(2):e0148936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148936. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26866365 Free PMC article.
-
The histone-like protein HU has a role in gene expression during the acid adaptation response in Helicobacter pylori.Helicobacter. 2017 Aug;22(4). doi: 10.1111/hel.12381. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Helicobacter. 2017. PMID: 28244177
-
Influence of Helicobacter pylori virulence factors CagA and VacA on pathogenesis of gastrointestinal disorders.Microb Pathog. 2018 Apr;117:43-48. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.02.016. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29432909 Review.
-
The use of microarrays for studying the pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori.Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 2003 Jan-Jun;45(1-2):24-9. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 17061518 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-8 is the single most up-regulated gene in whole genome profiling of H. pylori exposed gastric epithelial cells.BMC Microbiol. 2012 Jan 17;12:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-9. BMC Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22248188 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized recombinant production of the bacteriocin garvicin Q by Corynebacterium glutamicum.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1254882. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1254882. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38260893 Free PMC article.
-
The Helicobacter pylori autotransporter ImaA (HP0289) modulates the immune response and contributes to host colonization.Infect Immun. 2012 Jul;80(7):2286-96. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00312-12. Epub 2012 May 7. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22566509 Free PMC article.
-
The quorum-sensing molecule autoinducer 2 regulates motility and flagellar morphogenesis in Helicobacter pylori.J Bacteriol. 2007 Sep;189(17):6109-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00246-07. Epub 2007 Jun 22. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17586631 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Campylobacter jejuni genes contributing to acid adaptation by transcriptional profiling and genome-wide mutagenesis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Mar;74(5):1598-612. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01508-07. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18192408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akada, J. K., M. Shirai, H. Takeuchi, M. Tsuda, and T. Nakazawa. 2000. Identification of the urease operon in Helicobacter pylori and its control by mRNA decay in response to pH. Mol. Microbiol. 36:1071-1084. - PubMed
-
- Akopyants, N. S., S. W. Clifton, D. Kersulyte, J. E. Crabtree, B. E. Youree, C. A. Reece, N. O. Bukanov, E. S. Drazek, B. A. Roe, and D. E. Berg. 1998. Analyses of the cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol. 28:37-53. - PubMed
-
- Allan, E., C. L. Clayton, A. McLaren, D. M. Wallace, and B. W. Wren. 2001. Characterization of the low-pH responses of Helicobacter pylori using genomic DNA arrays. Microbiology 147:2285-2292. - PubMed
-
- Alm, R. A., L. S. Ling, D. T. Moir, B. L. King, E. D. Brown, P. C. Doig, D. R. Smith, B. Noonan, B. C. Guild, B. L. deJonge, G. Carmel, P. J. Tummino, A. Caruso, M. Uria-Nickelsen, D. M. Mills, C. Ives, R. Gibson, D. Merberg, S. D. Mills, Q. Jiang, D. E. Taylor, G. F. Vovis, and T. J. Trust. 1999. Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 397:176-180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

