Serotonin 1A receptor agonists reverse respiratory abnormalities in spinal cord-injured rats
- PMID: 12764106
- PMCID: PMC6741104
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-10-04182.2003
Serotonin 1A receptor agonists reverse respiratory abnormalities in spinal cord-injured rats
Abstract
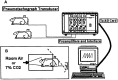
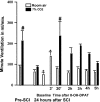
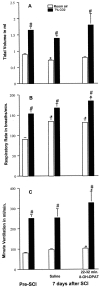
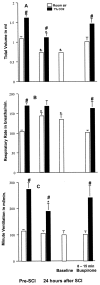
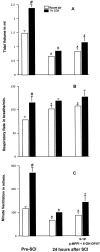
Contusion spinal cord injury (SCI) at T8 produces respiratory abnormalities in conscious rats breathing room air and challenged with CO2. In seeking ways to improve respiration after SCI, we tested drugs that stimulate serotonin 1A (5-HT1A) receptors, based on our previous findings that these agents can counteract respiratory depression produced by morphine overdose. Respiratory function was measured with a head-out plethysmograph system in conscious rats. T8 SCI rats (n = 5) showed decreased tidal volume (Vt; 0.90 +/- 0.02-0.66 +/- 0.03 ml; p < 0.05) and increased respiratory rate (f;91 +/- 3.7-132 +/- 5.7 breaths/min; p < 0.05) with room air ventilation at 24 hr after injury. They also exhibited a diminished response to the respiratory stimulating effect of 7% CO2; minute ventilation increased to 250 +/- 17 ml/min before, but only to 162 +/- 15 ml/min at 24 hr after SCI (p < 0.05). Respiratory deficits during room air ventilation were also observed at 7 d after injury (n = 3). Treatment with the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylmino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT; 250 microg/kg, i.p.) at 24 hr (n = 5) or 7 d (n = 3) after injury normalized Vt, f, and the respiratory response to 7% CO2. Identical results were obtained with another 5-HT1A receptor agonist, buspirone (1.5 mg/kg, i.p.; n = 3). In contrast, intraperitoneal saline vehicle administration (n = 5) showed no beneficial effects on SCI-impaired respiration. Finally, pretreatment with a specific antagonist of 5-HT1A receptors, 4-iodo-N-[2-[4-(methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-N-2-pyridinyl-benzamide (3 mg/kg, i.p.; n = 3) given 20 min before 8-OH-DPAT, prevented 8-OH-DPAT from restoring respiration to normal. Our results demonstrate that drugs that stimulate 5-HT1A receptors counteract respiratory abnormalities in conscious rats after SCI.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Respiratory abnormalities resulting from midcervical spinal cord injury and their reversal by serotonin 1A agonists in conscious rats.J Neurosci. 2005 May 4;25(18):4550-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5135-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15872102 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of morphine-induced apnea in the anesthetized rat by drugs that activate 5-hydroxytryptamine(1A) receptors.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Feb;292(2):704-13. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000. PMID: 10640309
-
Pharmacological characterization of in vivo properties of putative mixed 5-HT1A agonist/5-HT(2A/2C) antagonist anxiolytics. II. Drug discrimination and behavioral observation studies in rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Aug;282(2):747-59. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997. PMID: 9262338
-
Serotonin 1A Receptor Pharmacotherapy and Neuroplasticity in Spinal Cord Injury.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Apr 11;15(4):460. doi: 10.3390/ph15040460. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin receptors: guardians of stable breathing.Trends Mol Med. 2003 Dec;9(12):542-8. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2003.10.010. Trends Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 14659469 Review.
Cited by
-
T12-L3 Nerve Transfer-Induced Locomotor Recovery in Rats with Thoracolumbar Contusion: Essential Roles of Sensory Input Rerouting and Central Neuroplasticity.Cells. 2023 Dec 8;12(24):2804. doi: 10.3390/cells12242804. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132124 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged treatment with ligands affects ligand binding to the human serotonin(1A) receptor in Chinese hamster ovary cells.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006 May;26(3):247-57. doi: 10.1007/s10571-006-9002-7. Epub 2006 Apr 21. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16767512 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT2A receptors are concentrated in regions of the human infant medulla involved in respiratory and autonomic control.Auton Neurosci. 2009 May 11;147(1-2):48-55. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2009.01.004. Epub 2009 Feb 12. Auton Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19213611 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal interaction of respiratory and thermal regulation at rest and during exercise: role of a serotonin-gated spinoparabrachial thermoafferent pathway.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009 Dec 31;169(3):234-42. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2009.09.006. Epub 2009 Sep 19. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19770073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinal activation of serotonin 1A receptors enhances latent respiratory activity after spinal cord injury.J Spinal Cord Med. 2006;29(2):147-55. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2006.11753868. J Spinal Cord Med. 2006. PMID: 16739558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC ( 1995) A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma 12: 1–21. - PubMed
-
- Bégin R, Bureau MA, Lupien L, Lemieux B ( 1980) Control of breathing in Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. Am J Med 69: 227–234. - PubMed
-
- Daval G, Verge D, Basbaum AI, Bourgoin S, Hamon M ( 1987) Autoradiographic evidence of serotonin 1 binding sites on primary afferent fibres in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 83: 71–76. - PubMed
-
- Gale K, Kerasidis H, Wrathall JR ( 1985) Spinal cord contusion in the rat: behavioral analysis of functional neurological impairment. Exp Neurol 88: 123–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
