Location and size of dopaminergic and serotonergic cell populations are controlled by the position of the midbrain-hindbrain organizer
- PMID: 12764108
- PMCID: PMC6741088
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-10-04199.2003
Location and size of dopaminergic and serotonergic cell populations are controlled by the position of the midbrain-hindbrain organizer
Abstract
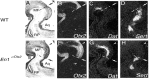
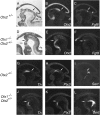
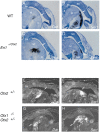
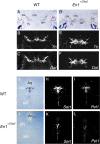
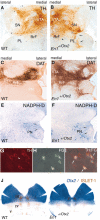
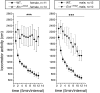
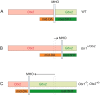
Midbrain dopaminergic and hindbrain serotonergic neurons play an important role in the modulation of behavior and are involved in a series of neuropsychiatric disorders. Despite the importance of these cells, little is known about the molecular mechanisms governing their development. During embryogenesis, midbrain dopaminergic neurons are specified rostral to the midbrain-hindbrain organizer (MHO), and hindbrain serotonergic neurons are specified caudal to it. We report that in transgenic mice in which Otx2 and accordingly the MHO are shifted caudally, the midbrain dopaminergic neuronal population expands to the ectopically positioned MHO and is enlarged. Complementary, the extension of the hindbrain serotonergic cell group is decreased. These changes are preserved in adulthood, and the additional, ectopic dopaminergic neurons project to the striatum, which is a proper dopaminergic target area. In addition, in mutants in which Otx2 and the MHO are shifted rostrally, dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons are relocated at the newly positioned MHO. However, in these mice, the size ratio between these two cell populations is changed in favor of the serotonergic cell population. To investigate whether the position of the MHO during embryogenesis is also of functional relevance for adult behavior, we tested mice with a caudally shifted MHO and report that these mutants show a higher locomotor activity. Together, we provide evidence that the position of the MHO determines the location and size of midbrain dopaminergic and hindbrain serotonergic cell populations in vivo. In addition, our data suggest that the position of the MHO during embryogenesis can modulate adult locomotor activity.
Figures
References
-
- Acampora D, Avantaggiato V, Tuorto F, Simeone A ( 1997) Genetic control of brain morphogenesis through Otx gene dosage requirement. Development 124: 3639–3650. - PubMed
-
- Barr CL, Xu C, Kroft J, Feng Y, Wigg K, Zai G, Tannock R, Schachar R, Malone M, Roberts W, Nothen MM, Grunhage F, Vandenbergh DJ, Uhl G, Sunohara G, King N, Kennedy JL ( 2001) Haplotype study of three polymorphisms at the dopamine transporter locus confirm linkage to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 49: 333–339. - PubMed
-
- Björklund A, Lindvall O ( 1984) Dopamine containing systems in the CNS. In: Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy, Vol II, Classical transmitter in the CNS, Pt I (Björklund A, Hökfeld, T, eds), pp 55–122. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
-
- Broccoli V, Boncinelli E, Wurst W ( 1999) The caudal limit of Otx2 expression positions the isthmic organizer. Nature 401: 164–168. - PubMed
-
- Castellanos FX, Tannock R ( 2002) Neuroscience of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: the search for endophenotypes. Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 617–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
