Vasopressin-induced cytoplasmic and nuclear calcium signaling in embryonic cortical astrocytes: dynamics of calcium and calcium-dependent kinase translocation
- PMID: 12764111
- PMCID: PMC6741105
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-10-04228.2003
Vasopressin-induced cytoplasmic and nuclear calcium signaling in embryonic cortical astrocytes: dynamics of calcium and calcium-dependent kinase translocation
Abstract
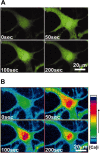
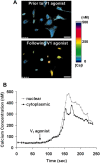
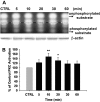
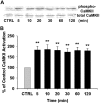
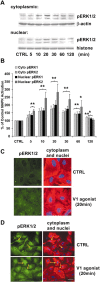
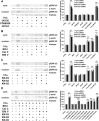
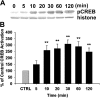
The present study sought to determine the downstream consequences of V1a vasopressin receptor (V1aR) activation of Ca2+ signaling in cortical astrocytes. Results of these analyses demonstrated that V1aR activation led to a marked increase in both cytoplasmic and nuclear Ca2+. We also investigated V1aR activation of Ca2+-activated signaling kinases, protein kinase C (PKC), Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), and the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases [MAPK and extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2)], their localization within cytoplasmic and nuclear compartments, and activation of their downstream nuclear target, the transcription factor cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB). Results of these analyses demonstrated that V1aR activation led to a significant rise in PKC, CaMKII, and ERK1/2 activation, with CaMKII and ERK1/2 demonstrating dynamic transport between cytoplasmic and nuclear compartments. Although no evidence of PKC translocation was apparent, PKC and CaMKs were required for activation and nuclear translocation of ERK1/2. Subsequent to CaMKII and ERK1/2 translocation to the nucleus, CREB activation occurred and was found to be dependent on upstream activation of ERK1/2 and CaMKs. These data provide the first systematic analysis of the V1aR-induced Ca2+ signaling cascade in cortical astrocytes. In addition, results of this study introduce a heretofore unknown effect of vasopressin, dynamic Ca2+ signaling between the cytoplasm and nucleus that leads to comparable dynamics of kinase activation and shuttling between cytoplasmic and nuclear compartments. Implications for development and regeneration induced by V1aR activation of CREB-regulated gene expression in cortical astrocytes are discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vasopressin-induced cytoplasmic and nuclear calcium signaling in cultured cortical astrocytes.Brain Res. 2002 Jul 5;943(1):117-31. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)02484-8. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12088846
-
Signaling Pathway for Endothelin-1- and Phenylephrine-Induced cAMP Response Element Binding Protein Activation in Rat Ventricular Myocytes: Role of Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptors and CaMKII.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(1):399-412. doi: 10.1159/000456422. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28214885
-
Suppression of proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in astrocytes by a V1 vasopressin receptor agonist: a cAMP response element-binding protein-dependent mechanism.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 3;24(9):2226-35. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4922-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14999073 Free PMC article.
-
Research advances on CaMKs-mediated neurodevelopmental injury.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Dec;98(12):3933-3947. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03865-5. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39292234 Review.
-
Calcium signaling in vasopressin-induced aquaporin-2 trafficking.Pflugers Arch. 2008 Jul;456(4):747-54. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0371-7. Epub 2007 Oct 24. Pflugers Arch. 2008. PMID: 17957381 Review.
Cited by
-
Promotion of Keratinocyte Proliferation by Tracheloside through ERK1/2 Stimulation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Jul 26;2018:4580627. doi: 10.1155/2018/4580627. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30147732 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional state-dependent ghrelin activation of vasopressin neurons via retrograde trans-neuronal-glial stimulation of excitatory GABA circuits.J Neurosci. 2014 Apr 30;34(18):6201-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3178-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24790191 Free PMC article.
-
Allopregnanolone-induced rise in intracellular calcium in embryonic hippocampal neurons parallels their proliferative potential.BMC Neurosci. 2008 Dec 3;9 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-9-S2-S11. BMC Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19090984 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the pharmacological profiles of arginine vasopressin and oxytocin analogs at marmoset, macaque, and human vasopressin 1a receptor.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jun;126:110060. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110060. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32145592 Free PMC article.
-
Klotho protein activates the PKC pathway in the kidney and testis and suppresses 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase gene expression.Endocrine. 2004 Dec;25(3):229-34. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:25:3:229. Endocrine. 2004. PMID: 15758250
References
-
- Abe K, Saito H ( 2000) The p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade is involved in the induction and maintenance of astrocyte stellation mediated by protein kinase C. Neurosci Res 36: 251–257. - PubMed
-
- Bachs O, Agell N, Carafoli E ( 1994) Calmodulin and calmodulin-binding proteins in the nucleus. Cell Calcium 16: 289–296. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ ( 1993) Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature 361: 315–325. - PubMed
-
- Bezzi P, Domercq M, Vesce S, Volterra A ( 2001) Neuron-astrocyte cross-talk during synaptic transmission: physiological and neuropathological implications. Prog Brain Res 132: 255–265. - PubMed
-
- Boer GJ ( 1985) Vasopressin and brain development: studies using the Brattleboro rat. Peptides 6: 49–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
