Osmotic regulation of estrogen receptor-beta in rat vasopressin and oxytocin neurons
- PMID: 12764114
- PMCID: PMC6741117
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-10-04261.2003
Osmotic regulation of estrogen receptor-beta in rat vasopressin and oxytocin neurons
Abstract
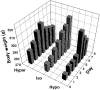
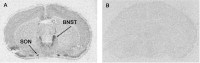
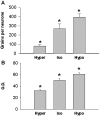
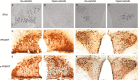
The vasopressin (VP) magnocellular neurosecretory cells (MNCs) in the supraoptic and paraventricular (PVN) nuclei are regulated by estrogen and exhibit robust expression of estrogen receptor (ER)-beta. In contrast, only approximately 7.5% of oxytocin (OT) MNCs express ER-beta. We examined the osmotic regulation of ER-beta mRNA expression in MNCs using quantitative in situ hybridization histochemistry. Hyper-osmolality induced via 2% hypertonic saline ingestion significantly decreased, whereas sustained hypo-osmolality induced via d-d-arginine VP and liquid diet increased ER-beta mRNA expression in MNCs (p < 0.05). Thus, the expression of ER-beta mRNA correlated inversely with changes in plasma osmolality. Because hyper-osmolality is a potent stimulus for VP and OT release, this suggests an inhibitory role for ER-beta in MNCs. Immunocytochemistry demonstrated that the decrease in ER-beta mRNA was translated into depletion of receptor protein content in hyper-osmotic animals. Numerous MNCs were positive for ER-beta in control animals, but they were virtually devoid of ER-beta-immunoreactivity (IR) in hyper-osmotic animals. The osmotically induced decrease in ER-beta expression was selective for MNCs because ER-beta-IR remained unaltered in PVN parvocellular neurons. Plasma estradiol and testosterone were not correlated with ER-beta mRNA expression after osmotic manipulation, suggesting that ER-beta expression was not driven by ligand availability. Expression of FOS-IR in MNCs with attenuated ER-beta-IR, and the absence of FOS-IR in parvocellular neurons that retain ER-beta-IR suggest a role for neuronal activation in the regulation of ER-beta expression in MNCs. Thus, osmotic modulation of ER-beta expression in MNCs may augment or attenuate an inhibitory effect of gonadal steroids on VP release.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Osmotic regulation of estrogen receptor-beta expression in magnocellular vasopressin neurons requires lamina terminalis.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2004 Mar;286(3):R465-73. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00478.2003. Epub 2003 Nov 6. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14604844
-
Epithelial Na⁺ sodium channels in magnocellular cells of the rat supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Feb 1;302(3):E273-85. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00407.2011. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22045317 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of oestrogen receptor-beta mRNA expression in rat paraventricular and supraoptic nucleus neurones following adrenal steroid manipulation and hyperosmotic stimulation.J Neuroendocrinol. 2004 May;16(5):472-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2004.01190.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15117341
-
Estrogen modulates oxytocin gene expression in regions of the rat supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei that contain estrogen receptor-beta.Prog Brain Res. 2002;139:15-29. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(02)39004-6. Prog Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12436923 Review.
-
Mechanical basis of osmosensory transduction in magnocellular neurosecretory neurones of the rat supraoptic nucleus.J Neuroendocrinol. 2015 Jun;27(6):507-15. doi: 10.1111/jne.12270. J Neuroendocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25712904 Review.
Cited by
-
Hormonal changes during menopause and the impact on fluid regulation.Reprod Sci. 2014 May;21(5):555-61. doi: 10.1177/1933719113518992. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Reprod Sci. 2014. PMID: 24492487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen receptors and the regulation of neural stress responses.Neuroendocrinology. 2012;96(2):111-8. doi: 10.1159/000338397. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Neuroendocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22538291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Foetal Mummification in Pregnant Dairy Cows Induces Variant Changes on the Hormonal Profile, Biochemical Parameters and Mineral Profile of the Dam.Vet Med Sci. 2025 May;11(3):e70304. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70304. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40278801 Free PMC article.
-
Osmoregulatory defect in adult mice associated with deficient prenatal expression of six2.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):R682-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00187.2011. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21653879 Free PMC article.
-
Selective gene expression in magnocellular neurons in rat supraoptic nucleus.J Neurosci. 2004 Aug 11;24(32):7174-85. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2022-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15306651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Ghoul WM, Meeker RB, Greenwood RS ( 1997) Differential expression of five N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit mRNAs in vasopressin and oxytocin neuroendocrine cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 44: 262–272. - PubMed
-
- Amico JA, Seif SM, Robinson AG ( 1981) Oxytocin in human plasma: correlation with neurophysin and stimulation with estrogen. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 52: 988 -993. - PubMed
-
- Bai G, Kusiak JW ( 1993) Cloning and analysis of the 5′ flanking sequence of the rat N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor 1 (NMDAR1) gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1152: 197–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
