Error monitoring using external feedback: specific roles of the habenular complex, the reward system, and the cingulate motor area revealed by functional magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 12764119
- PMCID: PMC6741115
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-10-04308.2003
Error monitoring using external feedback: specific roles of the habenular complex, the reward system, and the cingulate motor area revealed by functional magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
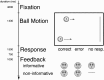
The dopaminergic system has been shown to be involved in the processing of rewarding stimuli, specifically of errors in reward prediction, in animal studies as well as in recent neuroimaging studies in humans. Furthermore, a specific role of dopamine in the human homolog of the rostral cingulate motor area (rCMA) was proposed in a recent model of error detection. Negative feedback as well as self-detected errors elicit a negative event-related brain potential probably generated in the rCMA. We performed two experiments using functional magnetic resonance imaging to investigate the brain activity related to negative and positive feedback in a dynamically adaptive motion prediction task. Whereas positive feedback raised hemodynamic activity in the ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens), negative feedback activated the rCMA, the inferior anterior insula, and the epithalamus (habenular complex). These data demonstrate the role of the habenular complex in the control of the human reward system, a function previously hypothesized on the basis of animal research. The rCMA reacted only to errors with negative feedback but not to errors without feedback, which ruled out an influence of response conflict or uncertainty on its role in error detection by external signals.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Knowing good from bad: differential activation of human cortical areas by positive and negative outcomes.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Jun;21(11):3161-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04152.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15978024
-
Elderly adults show higher ventral striatal activation in response to motor performance related rewards than young adults.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Nov 20;661:18-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.09.038. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28939388
-
The rewarding value of good motor performance in the context of monetary incentives.Neuropsychologia. 2012 Jul;50(8):1739-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.03.030. Epub 2012 May 6. Neuropsychologia. 2012. PMID: 22569215
-
Action sets and decisions in the medial frontal cortex.Trends Cogn Sci. 2004 Sep;8(9):410-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2004.07.009. Trends Cogn Sci. 2004. PMID: 15350242 Review.
-
Prediction error in reinforcement learning: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013 Aug;37(7):1297-310. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.03.023. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013. PMID: 23567522 Review.
Cited by
-
Language differences in the brain network for reading in naturalistic story reading and lexical decision.PLoS One. 2015 May 27;10(5):e0124388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124388. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26017384 Free PMC article.
-
Social manipulation of preference in the human brain.Neuron. 2013 May 8;78(3):563-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.03.023. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 23664619 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of MeCP2 at Ser421 contributes to chronic antidepressant action.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 10;32(41):14355-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2156-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23055506 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analytic clustering dissociates brain activity and behavior profiles across reward processing paradigms.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2020 Apr;20(2):215-235. doi: 10.3758/s13415-019-00763-7. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31872334 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as pharmacotherapeutic targets for the treatment of alcohol use disorders.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010 Mar;9(1):60-76. doi: 10.2174/187152710790966597. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20201817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aguirre GK, Zarahn E, D'Esposito M ( 1997) Empirical analysis of BOLD fMRI statistics, Vol II: spatially smoothed data collected under null-hypothesis and experimental conditions. NeuroImage 5: 199–212. - PubMed
-
- Berridge KC, Robinson TE ( 1998) What is the role of dopamine in reward: hedonic impact, reward learning, or incentive salience? Brain Res Brain Res Rev 28: 309–369. - PubMed
-
- Carter CS, Braver TS, Barch DM, Botvinick MM, Noll D, Cohen JD ( 1998) Anterior cingulate cortex, error detection, and the online monitoring of performance. Science 280: 747–749. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
