Calpain regulates enterocyte brush border actin assembly and pathogenic Escherichia coli-mediated effacement
- PMID: 12764139
- PMCID: PMC2727654
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M304616200
Calpain regulates enterocyte brush border actin assembly and pathogenic Escherichia coli-mediated effacement
Abstract
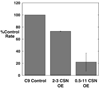
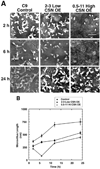
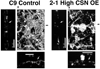
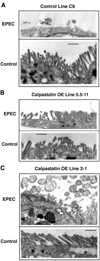
This study identifies calpain as being instrumental for brush border (BB) microvillus assembly during differentiation and effacement during bacterial pathogenesis. Calpain activity is decreased by 25-80% in Caco 2 lines stably overexpressing calpastatin, the physiological inhibitor of calpain, and the effect is proportional to the calpastatin/calpain ratio. These lines exhibit a 2.5-fold reduction in the rate of microvillus extension. Apical microvillus assembly is reduced by up to 50%, as measured by quantitative fluorometric microscopy (QFM) of ezrin, indicating that calpain recruits ezrin to BB microvilli. Calpain inhibitors ZLLYCHN2, MDL 28170, and PD 150606 block BB assembly and ezrin recruitment to the BB. The HIV protease inhibitor ritonavir, which inhibits calpain at clinically relevant concentrations, also blocks BB assembly, whereas cathepsin and proteasome inhibitors do not. Microvillus effacement is inhibited after exposure of calpastatin-overexpressing cells to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. These results suggest that calpain regulates BB assembly as well as pathological effacement, and indicate that it is an important regulator involved in HIV protease inhibitor toxicity and host-microbial pathogen interactions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Calpain mediates epithelial cell microvillar effacement by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2011 Nov 8;2:222. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00222. eCollection 2011. Front Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 22073041 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain regulates actin remodeling during cell spreading.J Cell Biol. 1998 May 4;141(3):647-62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.141.3.647. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9566966 Free PMC article.
-
Profilin-Mediated Actin Allocation Regulates the Growth of Epithelial Microvilli.Curr Biol. 2019 Oct 21;29(20):3457-3465.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.08.051. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31607529 Free PMC article.
-
Microvillus assembly. Not actin alone.Curr Biol. 1995 Jun 1;5(6):591-3. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00117-5. Curr Biol. 1995. PMID: 7552163 Review.
-
Regulation of the calpain-calpastatin system by membranes (review).Mol Membr Biol. 1996 Oct-Dec;13(4):217-24. doi: 10.3109/09687689609160599. Mol Membr Biol. 1996. PMID: 9116760 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of host calpain in the invasion of Cryptosporidium parvum.Microbes Infect. 2011 Jan;13(1):103-7. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2010.10.007. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Microbes Infect. 2011. PMID: 21087681 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of HIV protease inhibitor ritonavir on Akt-regulated cell proliferation in breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15;12(6):1883-96. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1167. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16551874 Free PMC article.
-
Store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) regulates melanoma proliferation and cell migration.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 21;9(2):e89292. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089292. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586666 Free PMC article.
-
The EHEC-host interactome reveals novel targets for the translocated intimin receptor.Sci Rep. 2014 Dec 18;4:7531. doi: 10.1038/srep07531. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25519916 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional patterns in both host and bacterium underlie a daily rhythm of anatomical and metabolic change in a beneficial symbiosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 2;107(5):2259-64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909712107. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133870 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

