An autoregulatory loop controls peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha expression in muscle
- PMID: 12764228
- PMCID: PMC165838
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1232352100
An autoregulatory loop controls peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha expression in muscle
Abstract
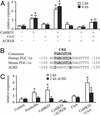
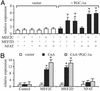
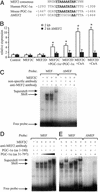
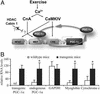
Skeletal muscle adapts to chronic physical activity by inducing mitochondrial biogenesis and switching proportions of muscle fibers from type II to type I. Several major factors involved in this process have been identified, such as the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CaMKIV), calcineurin A (CnA), and the transcriptional component peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha). Transgenic expression of PGC-1alpha recently has been shown to dramatically increase the content of type I muscle fibers in skeletal muscle, but the relationship between PGC-1alpha expression and the key components in calcium signaling is not clear. In this report, we show that the PGC-1alpha promoter is regulated by both CaMKIV and CnA activity. CaMKIV activates PGC-1alpha largely through the binding of cAMP response element-binding protein to the PGC-1alpha promoter. Moreover, we show that a positive feedback loop exists between PGC-1alpha and members of the myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) family of transcription factors. MEF2s bind to the PGC-1alpha promoter and activate it, predominantly when coactivated by PGC-1alpha. MEF2 activity is stimulated further by CnA signaling. These findings imply a unified pathway, integrating key regulators of calcium signaling with the transcriptional switch PGC-1alpha. Furthermore, these data suggest an autofeedback loop whereby the calcium-signaling pathway may result in a stable induction of PGC-1alpha, contributing to the relatively stable nature of muscle fiber-type determination.
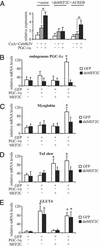
Figures
References
-
- Booth, F. W. & Thomason, D. B. (1991) Physiol. Rev. 71, 541-585. - PubMed
-
- Berchtold, M. W., Brinkmeier, H. & Muntener, M. (2000) Physiol. Rev. 80, 1215-1265. - PubMed
-
- Olson, E. N. & Williams, R. S. (2000) Cell 101, 689-692. - PubMed
-
- Hood, D. A. (2001) J. Appl. Physiol. 90, 1137-1157. - PubMed
-
- Corcoran, E. E. & Means, A. R. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 2975-2978. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

