Determinants of increased replicative capacity of serially passaged simian immunodeficiency virus with nef deleted in rhesus monkeys
- PMID: 12768002
- PMCID: PMC156171
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.12.6823-6835.2003
Determinants of increased replicative capacity of serially passaged simian immunodeficiency virus with nef deleted in rhesus monkeys
Abstract
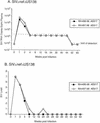
Most rhesus macaques infected with simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239 with nef deleted (either Delta nef or Delta nef Delta vpr Delta US [Delta 3]) control viral replication and do not progress to AIDS. Some monkeys, however, develop moderate viral load set points and progress to AIDS. When simian immunodeficiency viruses (SIVs) recovered from two such animals (one Delta nef and the other Delta 3) were serially passaged in rhesus monkeys, the SIVs derived from both lineages were found to consistently induce moderate viral loads and disease progression. Analysis of viral sequences in the serially passaged derivatives revealed interesting changes in three regions: (i) an unusually high number of predicted amino acid changes (12 to 14) in the cytoplasmic domain of gp41, most of which were in regions that are usually conserved; these changes were observed in both lineages; (ii) an extreme shortening of nef sequences in the region of overlap with U3; these changes were observed in both lineages; and (iii) duplication of the NF-kappa B binding site in one lineage only. Neither the polymorphic gp41 changes alone nor the U3 deletion alone appeared to be responsible for increased replicative capacity because recombinant SIVmac239 Delta nef, engineered to contain either of these changes, induced moderate viral loads in only one of six monkeys. However, five of six monkeys infected with recombinant SIVmac239 Delta nef containing both TM and U3 changes did develop persisting moderate viral loads. These genetic changes did not increase lymphoid cell-activating properties in the monkey interleukin-2-dependent T-cell line 221, but the gp41 changes did increase the fusogenic activity of the SIV envelope two- to threefold. These results delineate sequence changes in SIV that can compensate for the loss of the nef gene to partially restore replicative and pathogenic potential in rhesus monkeys.
Figures

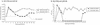
References
-
- Aiken, C., J. Konner, N. Landau, M. E. Lenburg, and D. Trono. 1994. Nef induces CD4 endocytosis: requirement for a critical dileucine motif in the membrane-proximal CD4 cytoplasmic domain. Cell 76:853-864. - PubMed
-
- Alexander, L., R. S. Veazey, S. Czajak, M. DeMaria, M. Rosenzweig, A. A. Lackner, R. C. Desrosiers, and V. G. Sasseville. 1999. Recombinant simian immunodeficiency virus expressing green fluorescent protein identifies infected cells in rhesus monkeys. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 15:11-21. - PubMed
-
- Alexander, L., E. Weiskopf, T. C. Greenough, N. C. Gaddis, M. R. Auerbach, M. H. Malim, S. J. O'Brien, B. D. Walker, J. L. Sullivan, and R. C. Desrosiers. 2000. Unusual polymorphisms in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 associated with nonprogressive infection. J. Virol. 74:4361-4376. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

