Promyelocytic leukemia protein mediates interferon-based anti-herpes simplex virus 1 effects
- PMID: 12768029
- PMCID: PMC156157
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.12.7101-7105.2003
Promyelocytic leukemia protein mediates interferon-based anti-herpes simplex virus 1 effects
Abstract
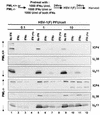
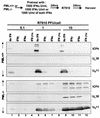
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) 1 disaggregates the nuclear domain 10 (ND10) nuclear structures and disperses its organizing promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML). An earlier report showed that ectopic overexpression of PML precludes the disaggregation of ND10 but has no effect on viral replication. PML has been reported to mediate the effects of interferon (IFN) and viral mutants lacking ICP0 (Delta alpha 0 mutants). To test the hypothesis that HSV disaggregates ND10 structures and disperses PML to preclude IFN-mediated antiviral effects, we tested the accumulation of viral proteins and virus yields from murine PML(+/+) and PML(-/-) cells mock treated or exposed to IFN-alpha, IFN-gamma, or both and infected with the wild-type or Delta alpha 0 mutant virus. We report the following results. (i) The levels of growth of wild-type and mutant viruses and of accumulation of viral proteins were not significantly different in untreated PML(+/+) and PML(-/-) cells. (ii) Major effects of IFN-alpha and -gamma were observed in PML(+/+) cells infected with the Delta alpha 0 mutant virus, and more minor effects were observed in cells infected with the wild-type virus. The effects of the IFNs on either wild-type or the mutant virus in PML(-/-) cells were minimal. (iii) The mixture of IFN-alpha and -gamma was more effective than either IFN alone, but again, the effect was more drastic in PML(+/+) cells than in PML(-/-) cells. We concluded that the anti-HSV state induced by exogenous IFN is mediated by PML and that the virus targets the ND10 structures and disseminates PML in order to preclude the establishment of the antiviral state induced by IFNs.
Figures
References
-
- Ahn, J. H., E. J. Brignole III, and G. S. Hayward. 1998. Disruption of PML subnuclear domains by the acidic IE1 protein of human cytomegalovirus is mediated through interaction with PML and may modulate a RING finger-dependent cryptic transactivator function of PML. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:4899-4913. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doucas, V., A. M. Ishov, A. Romo, H. Juguilon, M. D. Weitzman, R. M. Evans, and G. G. Maul. 1996. Adenovirus replication is coupled with the dynamic properties of the PML nuclear structure. Genes Dev. 10:196-207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA78766/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA83939/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA078766/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA87661/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA071692/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087661/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA071692/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA071933/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA088860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA88860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA078766/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA083939/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA71692/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

