Activated Notch1 inhibits p53-induced apoptosis and sustains transformation by human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncogenes through a PI3K-PKB/Akt-dependent pathway
- PMID: 12768030
- PMCID: PMC156194
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.12.7106-7112.2003
Activated Notch1 inhibits p53-induced apoptosis and sustains transformation by human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncogenes through a PI3K-PKB/Akt-dependent pathway
Abstract
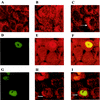
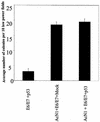
Activated Notch1 (AcN1) alleles cooperate with oncogenes from DNA tumor viruses in transformation of epithelial cells. AcN1 signaling has pleiotropic effects, and suggested oncogenic roles include driving proliferation through cyclin D1 or the generation of resistance to apoptosis on matrix withdrawal through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-PKB/Akt-dependent pathway. Here, we extend the antiapoptotic role for AcN1 by showing inhibition of p53-induced apoptosis and transactivation. Chemical inhibitors of the PI3K pathway block AcN1-induced inhibition of p53-dependent apoptosis and nuclear localization of Hdm2. We show that expression of wild-type p53 does not inhibit synergistic transformation by AcN1 and human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncogenes. We suggest that activation of Notch signaling may serve as an additional mechanism to inhibit wild-type p53 function in papillomavirus-associated neoplasia.
Figures

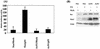
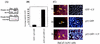
References
-
- Ashcroft, M., R. L. Ludwig, D. B. Woods, T. D. Copeland, H. O. Weber, E. J. MacRae, and K. H. Vousden. 2002. Phosphorylation of HDM2 by Akt. Oncogene 21:1955-1962. - PubMed
-
- Aster, J. C., and W. S. Pear. 2001. Notch signaling in leukemia. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 8:237-244. - PubMed
-
- Brazil, D. P., and B. A. Hemmings. 2001. Ten years of protein kinase B signalling: a hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26:657-664. - PubMed
-
- Daniel, B., A. Rangarajan, G. Mukherjee, E. Vallikad, and S. Krishna. 1997. The link between integration and expression of human papillomavirus type 16 genomes and cellular changes in the evolution of cervical intraepithelial neoplastic lesions. J. Gen. Virol. 78:1095-1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

