Targeted cytotoxic effect of anti-JL1 immunotoxin against a human leukemic cell line and its clinical implications
- PMID: 12768327
- PMCID: PMC11033006
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-003-0374-y
Targeted cytotoxic effect of anti-JL1 immunotoxin against a human leukemic cell line and its clinical implications
Abstract
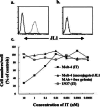
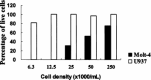
We have previously reported the identification of a unique thymocyte-specific surface molecule, JL1, which was detected using the monoclonal antibody (mAb), anti-JL1. Interestingly, JL1 was shown to be expressed in most leukemias, irrespective of their immunophenotype, and subpopulations of normal bone marrow (BM) mononuclear cells (MNCs). Here we investigated the potential usefulness of the anti-JL1 mAb as a therapeutic tool for leukemia. We demonstrated that the proliferation of cultured human leukemia cells was dramatically inhibited in vitro by anti-JL1 mAb conjugated with the polypeptide toxin, gelonin, but not by gelonin alone. We then systematically investigated the reactivity of the anti-JL1 mAb against normal human tissues to evaluate possible side effects along with various hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic tumor cell lines. All of 33 types of normal tissues except thymus and subpopulation of BM MNCs were clearly devoid of JL1 expression. Among tumor cell lines, all the nonhematopoietic cell lines tested were negative for JL1 expression, while some hematopoietic cell lines contained JL1 antigen. Collectively, the results showed the cytotoxic effects of anti-JL1-based immunotoxin against JL1-positive leukemic cells, sparing most normal tissues other than thymocytes and some BM MNCs. Therefore, we strongly suggest that gelonin-conjugated anti-JL1 mAb immunotoxin could be developed as a potential immunotherapeutic agent in the treatment of various types of JL1-positive acute leukemias.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immunotherapeutic potential of JL1, a thymocyte surface protein, for leukemia.J Korean Med Sci. 1998 Oct;13(5):455-8. doi: 10.3346/jkms.1998.13.5.455. J Korean Med Sci. 1998. PMID: 9811172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A cell surface molecule, JL1; a specific target for diagnosis and treatment of leukemias.Leukemia. 1998 Oct;12(10):1583-90. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401161. Leukemia. 1998. PMID: 9766503
-
In vivo anti-leukemic efficacy of anti-CD7-pokeweed antiviral protein immunotoxin against human T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency.Leukemia. 1993 Feb;7(2):298-309. Leukemia. 1993. PMID: 7678882
-
Humanized M195 monoclonal antibody conjugated to recombinant gelonin: an anti-CD33 immunotoxin with antileukemic activity.Clin Cancer Res. 1998 Aug;4(8):1971-6. Clin Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9717827
-
Large scale manufacturing of TXU(anti-CD7)-pokeweed antiviral protein (PAP) immunoconjugate for clinical trials.Leuk Lymphoma. 1997 Oct;27(3-4):275-302. doi: 10.3109/10428199709059683. Leuk Lymphoma. 1997. PMID: 9402326 Review.
Cited by
-
The Incidence and Immunophenotypic and Genetic Features of JL1 Expressing Cells and the Therapeutic Potential of an Anti-JL1 Antibody in De Novo Pediatric Acute Leukemias.Ann Lab Med. 2019 Jul;39(4):358-366. doi: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.4.358. Ann Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 30809981 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotoxins for targeted cancer therapy.AAPS J. 2006 Aug 18;8(3):E532-51. doi: 10.1208/aapsj080363. AAPS J. 2006. PMID: 17025272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of JL1 in Burkitt lymphoma is associated with improved overall survival.Virchows Arch. 2011 Oct;459(4):353-9. doi: 10.1007/s00428-011-1134-6. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Virchows Arch. 2011. PMID: 21814778
-
JL1 Antigen Expression on Bone Marrow Lymphoma Cells from Patients With Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.Ann Lab Med. 2020 Jan;40(1):1-6. doi: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.1.1. Ann Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 31432632 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of a developmentally regulated epitope of CD43 for the treatment of acute leukemia.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011 Dec;60(12):1697-706. doi: 10.1007/s00262-011-1066-7. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011. PMID: 21710258 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

