Effects of methyl p-hydroxybenzoate (methyl paraben) on Ca2+ concentration and histamine release in rat peritoneal mast cells
- PMID: 12770943
- PMCID: PMC1573847
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705248
Effects of methyl p-hydroxybenzoate (methyl paraben) on Ca2+ concentration and histamine release in rat peritoneal mast cells
Abstract
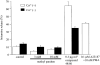
1 Mechanisms of methyl p-hydroxybenzoate (methyl paraben) action in allergic reactions were investigated by measuring the intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) and histamine release in rat peritoneal mast cells (RPMCs). 2 In the presence or absence of extracellular Ca(2+), methyl paraben (0.1-10 mM) increased [Ca(2+)](i), in a concentration-dependent manner. Under both the conditions, methyl paraben alone did not evoke histamine release. 3 In RPMCs pretreated with a protein kinase C (PKC) activator (phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) 3 and 10 nM), methyl paraben (0.3-3 mM) induced histamine release. However, a high concentration (10 mM) of the agent did not increase the histamine release. 4 U73122 (0.1 and 0.5 micro M), an inhibitor of phospholipase C (PLC), significantly inhibited the methyl paraben-induced histamine release in PMA-pretreated RPMCs. U73343 (0.5 micro M), an inactive analogue of U73122, did not inhibit the histamine release caused by methyl paraben. 5 In Ca(2+)-free solution, PLC inhibitors (U73122 0.1 and 0.5 micro M, D609 1-10 micro M) inhibited the methyl paraben-induced increase in [Ca(2+)](i), whereas U73343 (0.5 micro M) did not. 6 Xestospongin C (2-20 micro M) and 2 aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (30 and 100 micro M), blockers of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP(3)) receptor, inhibited the methyl paraben-induced increase in [Ca(2+)](i) in Ca(2+)-free solution. 7 In conclusion, methyl paraben causes an increase in [Ca(2+)](i), which may be due to release of Ca(2+) from storage sites by IP(3) via activation of PLC in RPMCs. In addition, methyl paraben possibly has some inhibitory effects on histamine release via unknown mechanisms.
Figures



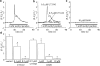

Similar articles
-
Two distinct signaling pathways for regulation of spontaneous local Ca2+ release by phospholipase C in airway smooth muscle cells.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Jan;453(4):531-41. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0130-1. Epub 2006 Nov 9. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17093969
-
ATP-inhibition of M current in frog sympathetic neurons involves phospholipase C but not Ins P(3), Ca(2+), PKC, or Ras.J Neurophysiol. 2002 Jul;88(1):277-88. doi: 10.1152/jn.2002.88.1.277. J Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 12091553
-
Dual regulation of the Na+/H(+)-exchange in rat peritoneal mast cells: role of protein kinase C and calcium on pHi regulation and histamine release.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Jul;118(6):1327-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15541.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8832053 Free PMC article.
-
The Na+/K(+)-pump in rat peritoneal mast cells: some aspects of regulation of activity and cellular function.Dan Med Bull. 1995 Nov;42(5):441-54. Dan Med Bull. 1995. PMID: 8747801 Review.
-
[Recent advances in the research on histamine release].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1991 Sep;98(3):197-207. doi: 10.1254/fpj.98.3_197. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1991. PMID: 1720758 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Anti-anaphylactic effects of Trichilia monadelpha (Thonn.) J. J. De Wilde extracts on rodent models of anaphylaxis.Res Pharm Sci. 2016 Oct;11(5):397-404. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.192491. Res Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27920822 Free PMC article.
-
A derivatization-enhanced detection strategy in mass spectrometry: analysis of 4-hydroxybenzoates and their metabolites after keratinocytes are exposed to UV radiation.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 6;7:39907. doi: 10.1038/srep39907. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28057923 Free PMC article.
-
Antianaphylactic and mast cell stabilization activity of Strychnos potatorum Linn. seed.Pharmacognosy Res. 2011 Jul;3(3):208-13. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.85011. Pharmacognosy Res. 2011. PMID: 22022171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AKITA M., SASAKI S., MATSUYAMA S., MIZUSHIMA S. SecA interacts with secretory proteins by recognizing the positive charge at the amino terminus of the signal peptide in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:8164–8169. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous Preservation, sterilization and stability testing of ophthalmic preparations. Int. J. Pharm. Compounding. 1998;2:192–195. - PubMed
-
- BEAVEN M.A., CUNHA-MELO J.R. Membrane phosphoinositide-activated signals in mast cells and basophils. Prog. Allergy. 1988;42:123–184. - PubMed
-
- BERRIDGE M.J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993;361:315–325. - PubMed
-
- BLEASDALE J.E., THAKUR N.R., GREMBAN R.S., BUNDY G.L., FITZPATRICK F.A., SMITH R.J., BUNTING S. Selective inhibition of receptor-coupled phospholipase C-dependent processes in human platelets and polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1990;255:756–768. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

