Effects of methyl p-hydroxybenzoate (methyl paraben) on Ca2+ concentration and histamine release in rat peritoneal mast cells
- PMID: 12770943
- PMCID: PMC1573847
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705248
Effects of methyl p-hydroxybenzoate (methyl paraben) on Ca2+ concentration and histamine release in rat peritoneal mast cells
Abstract
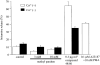
1 Mechanisms of methyl p-hydroxybenzoate (methyl paraben) action in allergic reactions were investigated by measuring the intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) and histamine release in rat peritoneal mast cells (RPMCs). 2 In the presence or absence of extracellular Ca(2+), methyl paraben (0.1-10 mM) increased [Ca(2+)](i), in a concentration-dependent manner. Under both the conditions, methyl paraben alone did not evoke histamine release. 3 In RPMCs pretreated with a protein kinase C (PKC) activator (phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) 3 and 10 nM), methyl paraben (0.3-3 mM) induced histamine release. However, a high concentration (10 mM) of the agent did not increase the histamine release. 4 U73122 (0.1 and 0.5 micro M), an inhibitor of phospholipase C (PLC), significantly inhibited the methyl paraben-induced histamine release in PMA-pretreated RPMCs. U73343 (0.5 micro M), an inactive analogue of U73122, did not inhibit the histamine release caused by methyl paraben. 5 In Ca(2+)-free solution, PLC inhibitors (U73122 0.1 and 0.5 micro M, D609 1-10 micro M) inhibited the methyl paraben-induced increase in [Ca(2+)](i), whereas U73343 (0.5 micro M) did not. 6 Xestospongin C (2-20 micro M) and 2 aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (30 and 100 micro M), blockers of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP(3)) receptor, inhibited the methyl paraben-induced increase in [Ca(2+)](i) in Ca(2+)-free solution. 7 In conclusion, methyl paraben causes an increase in [Ca(2+)](i), which may be due to release of Ca(2+) from storage sites by IP(3) via activation of PLC in RPMCs. In addition, methyl paraben possibly has some inhibitory effects on histamine release via unknown mechanisms.
Figures



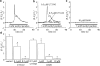

References
-
- AKITA M., SASAKI S., MATSUYAMA S., MIZUSHIMA S. SecA interacts with secretory proteins by recognizing the positive charge at the amino terminus of the signal peptide in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:8164–8169. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous Preservation, sterilization and stability testing of ophthalmic preparations. Int. J. Pharm. Compounding. 1998;2:192–195. - PubMed
-
- BEAVEN M.A., CUNHA-MELO J.R. Membrane phosphoinositide-activated signals in mast cells and basophils. Prog. Allergy. 1988;42:123–184. - PubMed
-
- BERRIDGE M.J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993;361:315–325. - PubMed
-
- BLEASDALE J.E., THAKUR N.R., GREMBAN R.S., BUNDY G.L., FITZPATRICK F.A., SMITH R.J., BUNTING S. Selective inhibition of receptor-coupled phospholipase C-dependent processes in human platelets and polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1990;255:756–768. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

