Castration decreases amylase release associated with muscarinic acetylcholine receptor downregulation in rat parotid gland
- PMID: 12770945
- PMCID: PMC1573856
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705260
Castration decreases amylase release associated with muscarinic acetylcholine receptor downregulation in rat parotid gland
Abstract
1 The mechanism and receptor subtypes involved in carbachol-stimulated amylase release and its changes after castration were studied in parotid slices from male rats. 2 Carbachol induced both amylase release and inositol phosphate (IP) accumulation in parotid slices from control and castrated rats, but castration induced a decrease of carbachol maximal effect. The effect of castration was reverted by testosterone replacement. 3 The selective M(1) and M(3) muscarinic receptor antagonists, pirenzepine and 4-diphenylacetoxy-N-methylpiperidine methiodide, respectively, inhibited carbachol-stimulated amylase release and IP accumulation in a dose-dependent manner in parotid slices from control and castrated rats. 4 A diminution of binding sites of muscarinic receptor in parotid membrane from castrated rats was observed. Competition binding assays showed that both, M(1) and M(3) muscarinic receptor subtypes are expressed in membranes of parotid glands from control and castrated rats, M(3) being the greater population. 5 These results suggest that amylase release induced by carbachol in parotid slices is mediated by phosphoinositide accumulation. This mechanism appears to be triggered by the activation of M(1) and M(3) muscarinic receptor subtypes. Castration induced a decrease of the maximal effect of carbachol evoked amylase release and IP accumulation followed by a diminution in the number of parotid gland muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
Figures
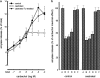
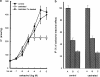
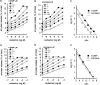
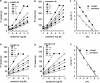

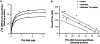
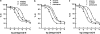
Similar articles
-
Influence of experimental periodontitis on cholinergic stimulation of K⁺ release in rat parotid glands.Auton Neurosci. 2012 Jul 2;169(1):43-8. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2012.03.004. Epub 2012 Apr 16. Auton Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22513211
-
Activation of nitric oxide synthase through muscarinic receptors in rat parotid gland.Eur J Pharmacol. 2002 Mar 29;439(1-3):27-33. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(02)01375-4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11937089
-
Carbachol stimulates inositol phosphate formation in rat thalamus slices through muscarinic M3-receptor activation.Neurosci Lett. 1996 Jul 26;213(1):29-32. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(96)12824-x. Neurosci Lett. 1996. PMID: 8844705
-
Cholinergic regulation of Na+-K+-ATPase activity in rat parotid gland: changes after castration.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Feb 13;486(1):99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2003.12.009. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14751414
-
An overview of autonomic regulation of parotid gland activity: influence of orchiectomy.Cells Tissues Organs. 2006;182(3-4):117-28. doi: 10.1159/000093962. Cells Tissues Organs. 2006. PMID: 16914915 Review.
Cited by
-
Cholinergic neurons excite cortically projecting basal forebrain GABAergic neurons.J Neurosci. 2014 Feb 19;34(8):2832-44. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3235-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24553925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BERNFELD P. Enzymes of starch degradation and synthesis. Adv Enzymol. 1951;12:379–428. - PubMed
-
- BROOKS J.C., BROOKS M., PISKOROWSKI J., WATSON J.D. Amylase secretion by cultured porcine parotid cells. Arch. Oral Biol. 1995;40:425–432. - PubMed
-
- BUSCH L., WALD M., BORDA E. Influence of castration on the response of the rat vas deferens to fluoxetine. Pharmacol. Res. 2000;42:305–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

